Doppler Intro
12PHYS - Wave Systems
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Mahi Tuatahi
- Work on Textbook 4a
- Hand in your homework!
The Doppler Effect
- When the frequency of a wave is altered due to relative motion between the object and the observer
- Think: the siren on an ambulance as it drives past!
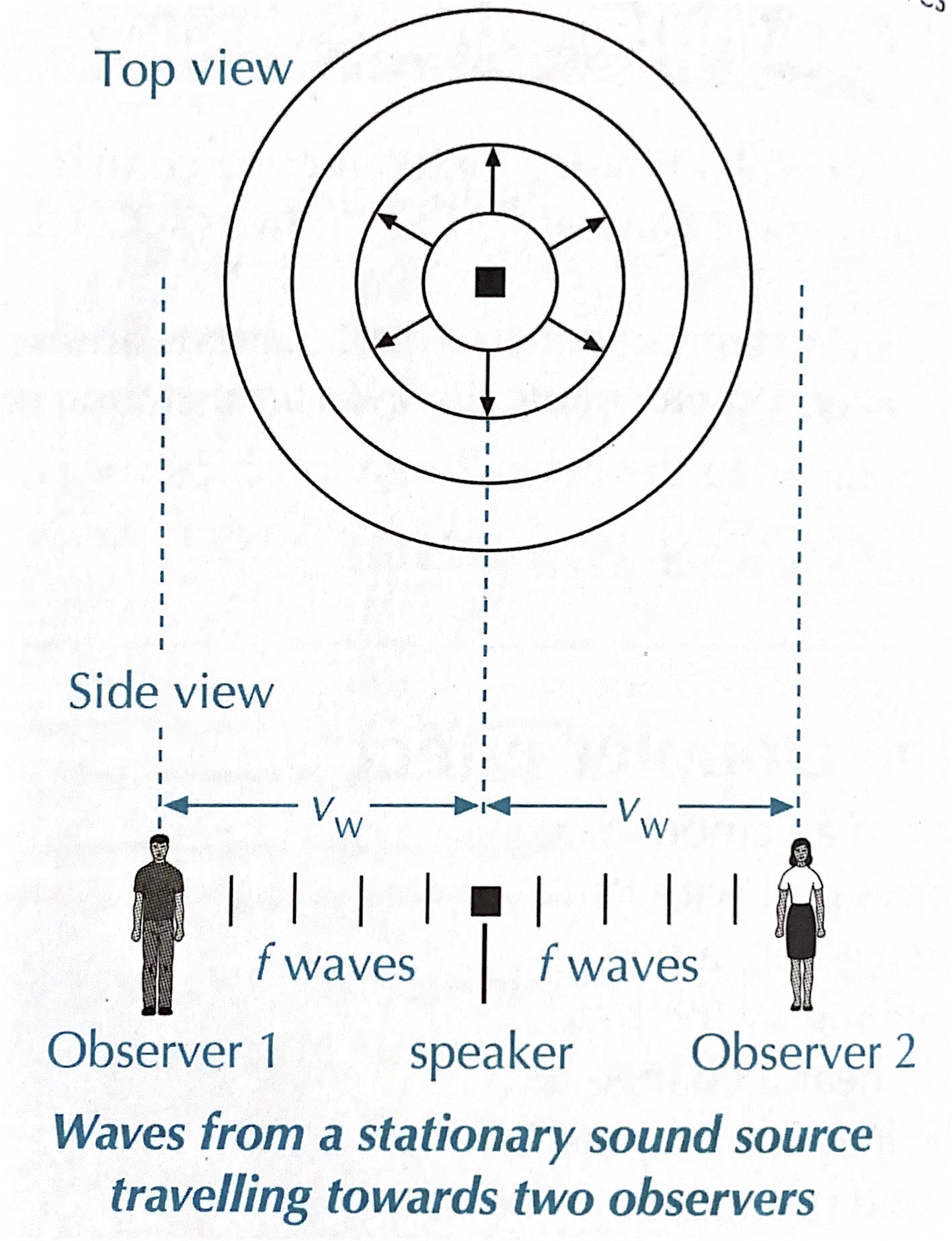
A Diagram

- Describe the wavelength and thus the frequency (pitch) in each location.
- In Front:
- Behind:
- Perpendicular:
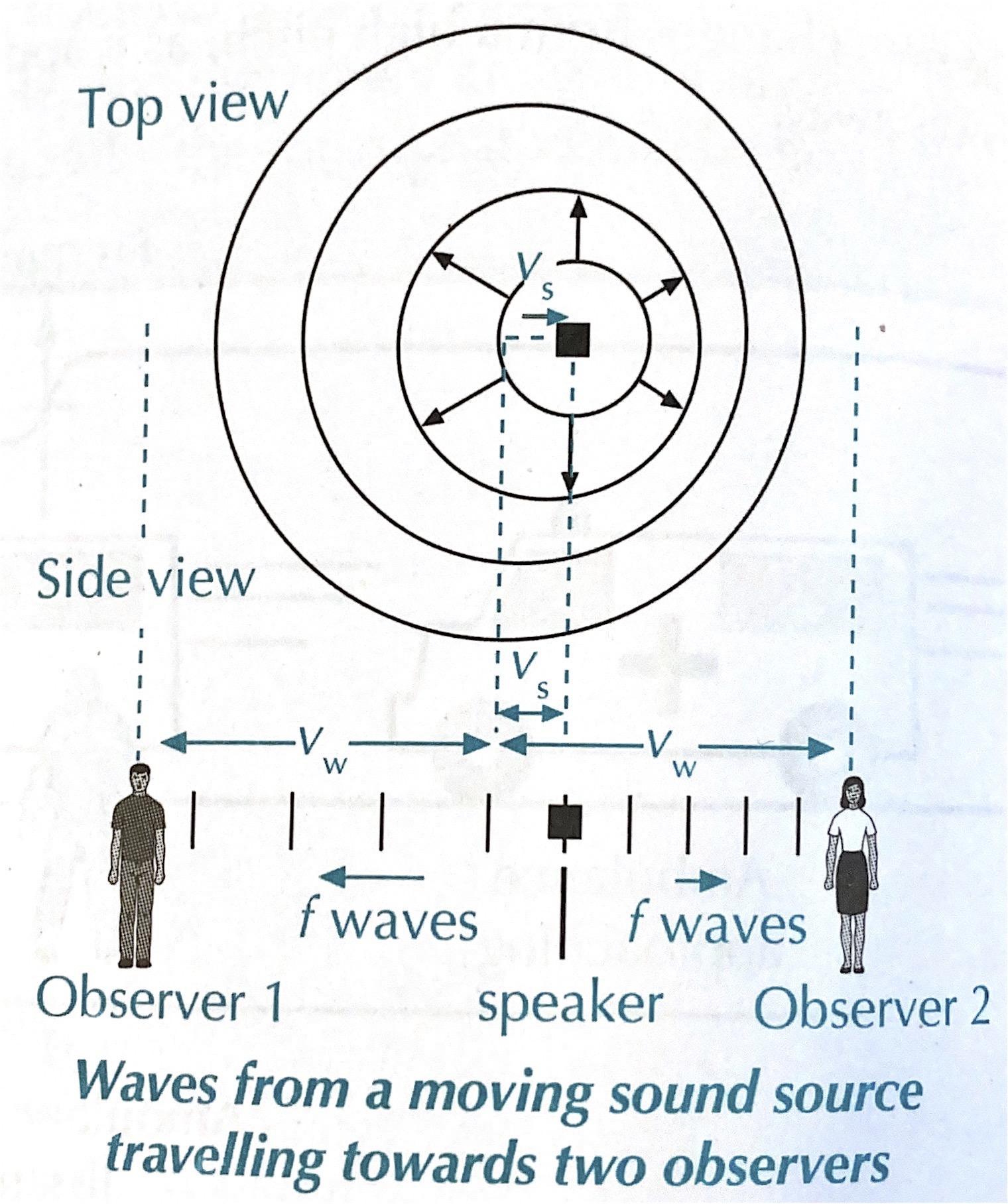
A Diagram

- In Front:
The wavelength is compressed: a higher frequency (pitch) is heard. - Behind:
The wavelength is expanded/rarefacted: a lower frequency (pitch) is heard. - Perpendicular:
The object is neither moving away or towards so the wavelength is not changed, so the wavelength is not changed and the original frequency is heard.
What is Observed?
- Sound: As a car approaches, the wavefront is compressed and the frequency is increased (pitch increases). As it passes, the wavefront is expanded, the frequency thus decreases (pitch decreases).
- Light: Doppler for light is also known as redshift: a star moving towards us has an increased frequency (bluer light), and a star moving away from us has a decreased frequency (redder light)
The Equations
- To work with the Doppler effect we will need to be confident using the equations we learned last week!
- If you do not have these equations in your book, copy them down and include the units for each variable.
\[ \begin{aligned} v &= f\lambda \newline f &= \frac{1}{T} \end{aligned} \]
Pātai: Speeding Tickets
Police can use radar guns to measure the amount of compression or expansion of the frequency due to the relative motion of the offending car.
- The gun emits waves with \(f=100MHz\). What wavelength is this?
- The gun reads \(f=125MHz\) when the car is approaching. What wavelength is this?
- The gun reads \(f=75MHz\) when the car is receding. What wavelength is this?
Converting Units
- Convert \(1000m\) into \(Mm\)
- Convert \(1000m\) into \(mm\)
- Convert \(1Gm\) into \(nm\)
- Convert \(620 \mu m\) into \(km\)
- Convert \(0.012km\) into \(nm\)
