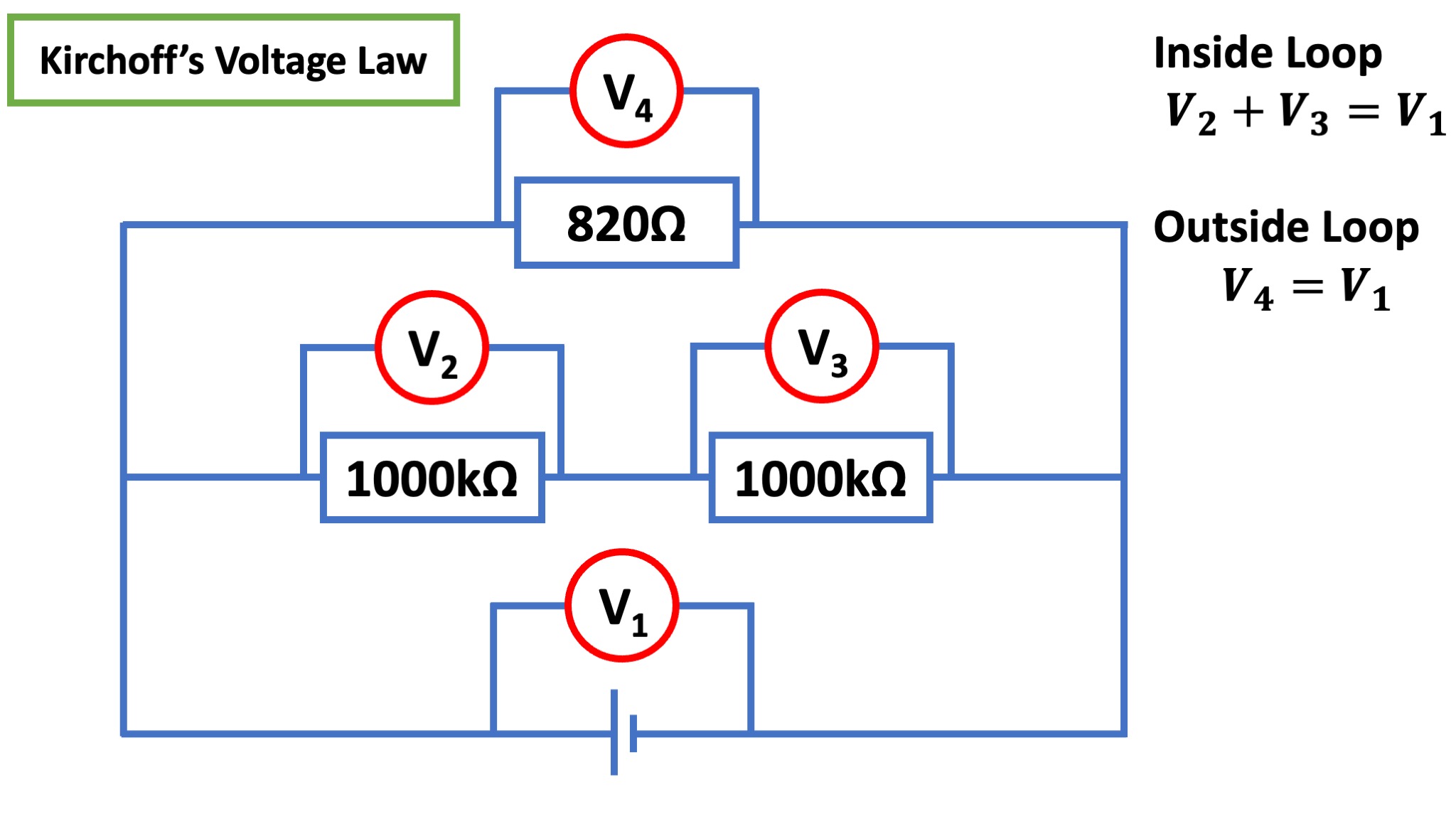
Kirchoff’s Voltage Law
12PHYS - Electricity
Finn Le Sueur
2024
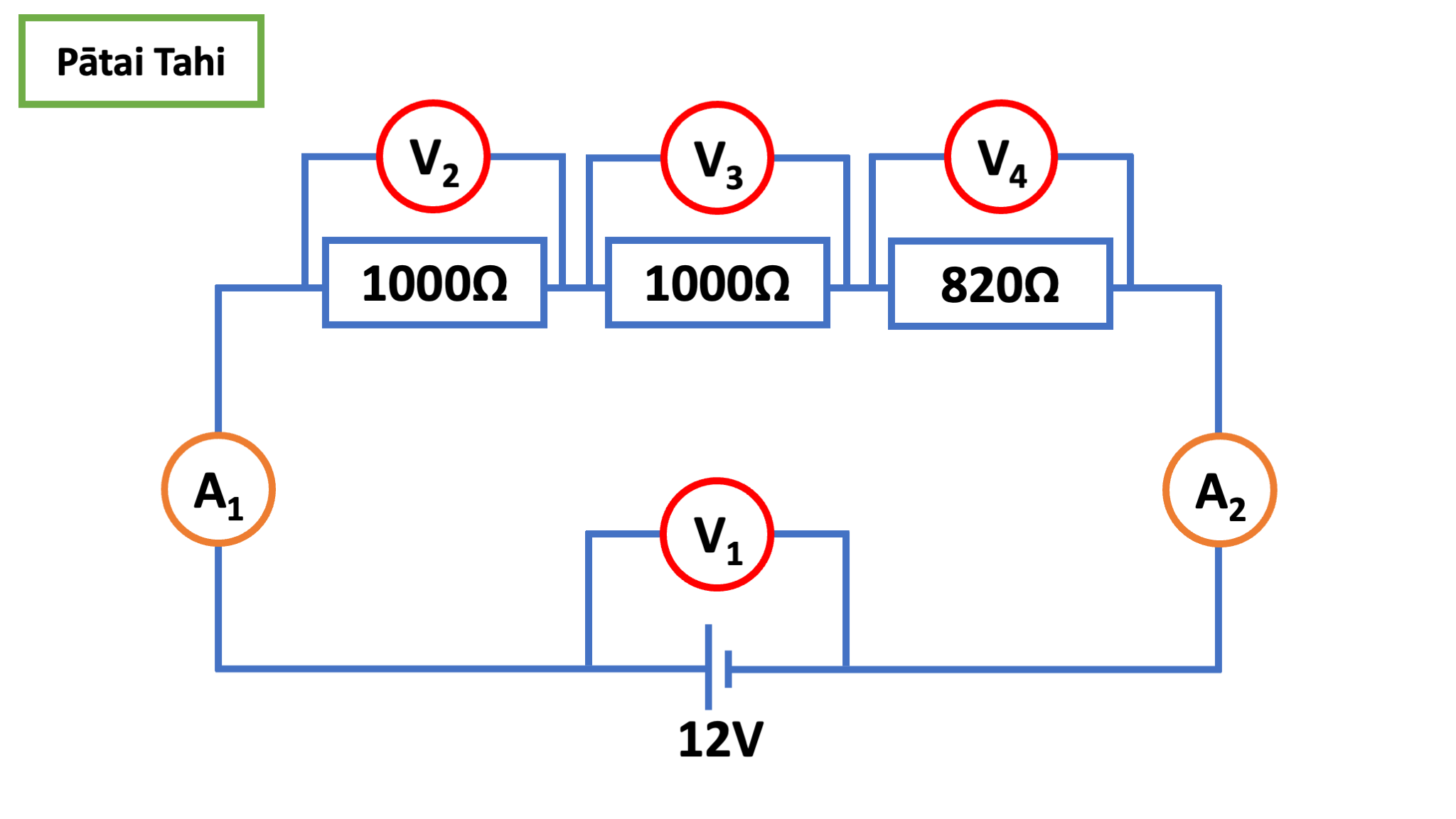
Mahi Tuatahi
Calculate the voltage used by each resistor.
Strategy: Start by calculating the total
resistance and the total current.
Kirchoff’s Laws: Voltage
The sum of the potential differences (voltages) in any closed loop is zero.
OR: That is to say, over a loop, the full voltage (energy) of the power supply must be consumed.
\[ \begin{aligned} V_{1} + V_{2} + V_{3} &= 0 \newline V_{1} + V_{4} &= 0 \end{aligned} \]
| Series Circuit | Parallel Circuit | |
|---|---|---|
| Current (I) in Amperes, \(A\) | Same through all components | Adds up to the supply |
| Voltage (V), in Volts, \(V\) | Adds up to the supply | Same across all equi-resistant paths |
| Resistance (R) in Ohms, \(\Omega\) | Combine to give more resistance (\(R_{T}=R_{1}+R_{2}+...\)) | Combine to give less resistance (\(\frac{1}{R_{T}}=\frac{1}{R_{1}}+\frac{1}{R_{2}}+...\)) |
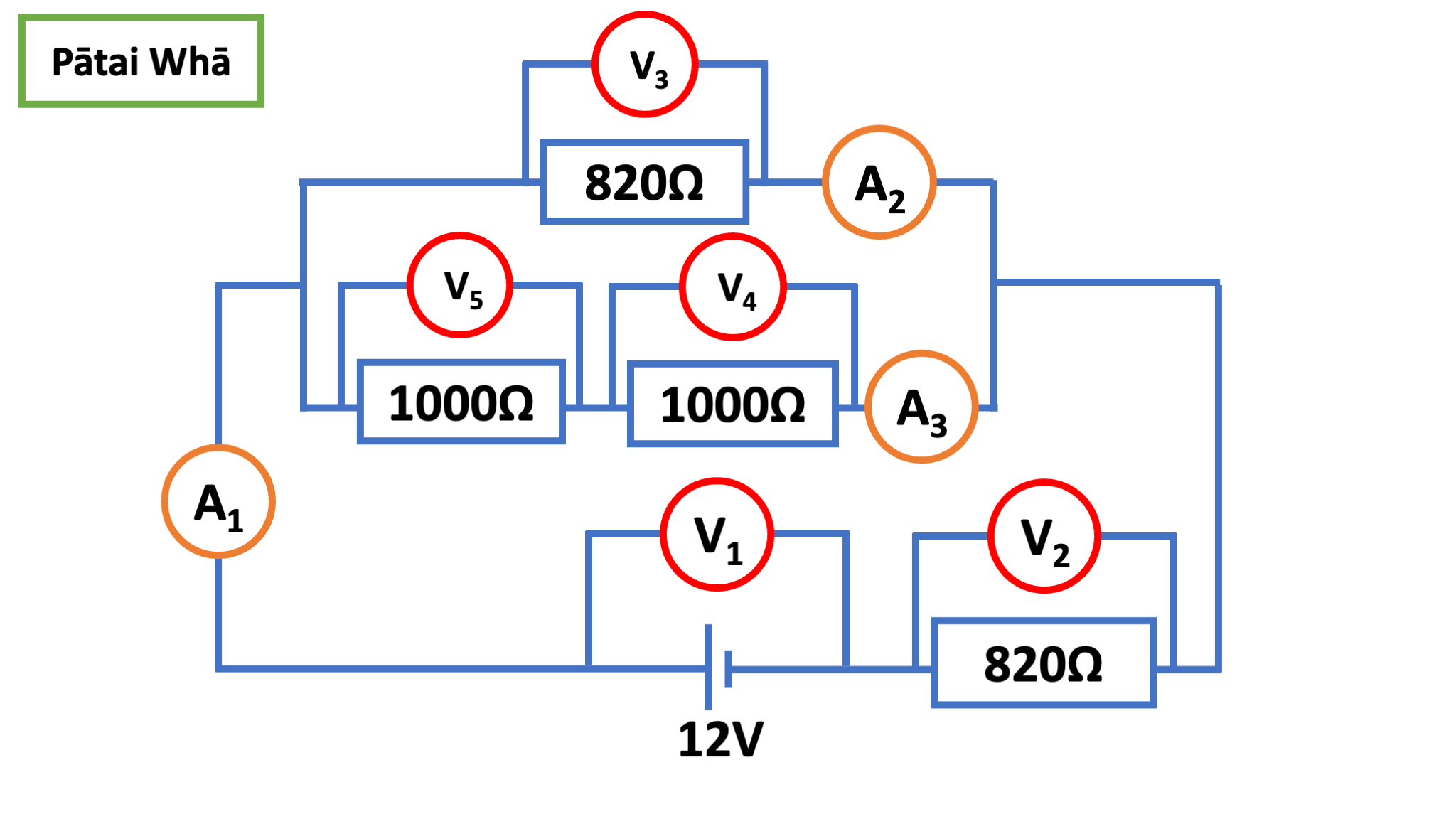
Pātai: Harder
Calculate all unknown values.
Strategy: You
should start by calculating the total resistance and total current.
Then, calculate the voltage used by the resistor in series with the
power supply.
Practice
- Textbook Activity 18B Q1, 3
- Homework Booklet: B1
- Fast Finishers: B3
Homework: A5, B2 due Monday!
Confirming Kirchoff’s Voltage Law
- Collect a Kirchoff’s Voltage Law sheet from the front.
- In a small group set up a station with a hardmat to protect the bench.
- Follow the instructions to set up each circuit in turn, take the required measurements and answer Task 1-4.