Types of Lava
Extreme Earth Events - 12ESS
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Akoranga 8 Mahi Tuatahi
- Open the Viscosity of Lava research document on Google Classroom
- Use it to create 2x bullet points for each section of your handout
Lava Flows & Eruptions

- How explosive a volcanic eruption is, and how far the lava will travel depends on the viscosity
- Viscosity: A measure of how
liquid/or not the material is
- High viscosity –> thick, molassas-like substance
- Low viscosity –> like water
Silica Content
- Silica is a silicon-oxygen compound found in rock.
- It has the greatest effect on lava viscosity.
- High silica content –> high viscosity.
- The particles are more tightly bound, this means it moves slower and is more explosive.
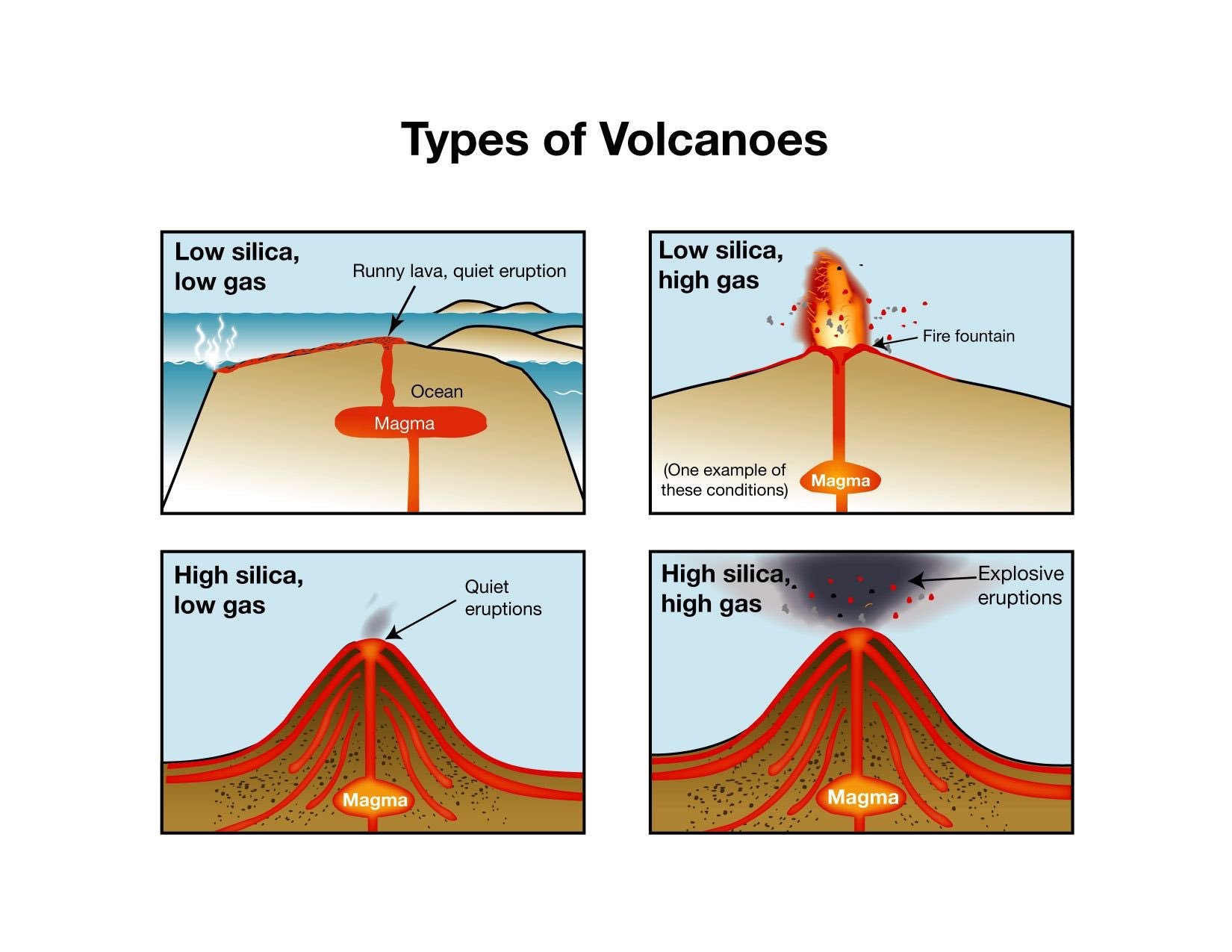
Gas Content
- Typically water, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide
- Gas can be compressed into a liquid (like soda), under the Earth
- As the magma rises and the pressure is released, the gas will try escape the magma (highly explosive)
- Magma with high gas content is not very viscous, but becomes more viscous as the gas escapes

Water Content
- Water is introduced through subduction of oceanic plates into the mantle
- Higher water content –> lower viscosity
- Think of this as diluting honey with water

Temperature
- Hot –> higher viscosity
- Magma composed of melted crust has a lower temperature
- Magma composed of melted mantle rocks has a higher temperature


Types of Lava
- Different minerals have different levels of silica in them
- Recall: silica has the greatest effect on viscosity (therefore shape & explosiveness) of a volcano
Basaltic
- Lower silica content
- Typically less than 52%
- Often found at divergent plate boundaries/hot spots
- Less viscous lava/less explosive eruptions
- Fissure/dome volcanoes

Andesitic
- Dark grey rock
- 52-66% silica
- Often found at subduction zones without rising to the surface
- Medium viscosity/medium explositive
- Stratovolcanoes

Rhyolitic
- Typically higher than 66% silica content
- Grey/pink in colour
- Found at convergent boundaries where subducted crust then rises to the surface
- Strato/composite volcanoes


Task / Ngohe
- Collect a Volcano Composition and Silica Content worksheet from the front
- Cut and glue it into your book
- Put paper cuttings (uncrumpled) in the recycling bin
- Use your knowledge from these notes and your previous worksheet to help you answer the questions!