Measuring Earthquakes
Extreme Earth Events - 12ESS
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Akoranga 18 Mahi Tuatahi
- Outline why earthquakes occur.
- Explain what prevents tectonic plates from moving in a smooth, constant manner.
- Define the term fault.
- Explain the difference between an earthquake’s focus and epicenter.
- What happens to wet, loose soil during an earthquake?
Whakatika
- Outline why earthquakes
occur.
Earthquakes occur when two or more tectonic plates move against each other. - Explain what prevents tectonic plates from
moving in a smooth, constant manner.
Friction between the two plates prevents constant movement. - Define the term
fault.
A crack in the Earth’s crust due to TP movement - Explain the difference between an
earthquake’s focus and epicenter.
The focus is the place underground where the earthquake occurs. The epicenter is on the surface directly above the focus. - What happens to wet, loose soil during an
earthquake?
Liquefaction
Te Whāinga Ako
- How earthquakes are measured
Write the date and te whāinga ako in your book
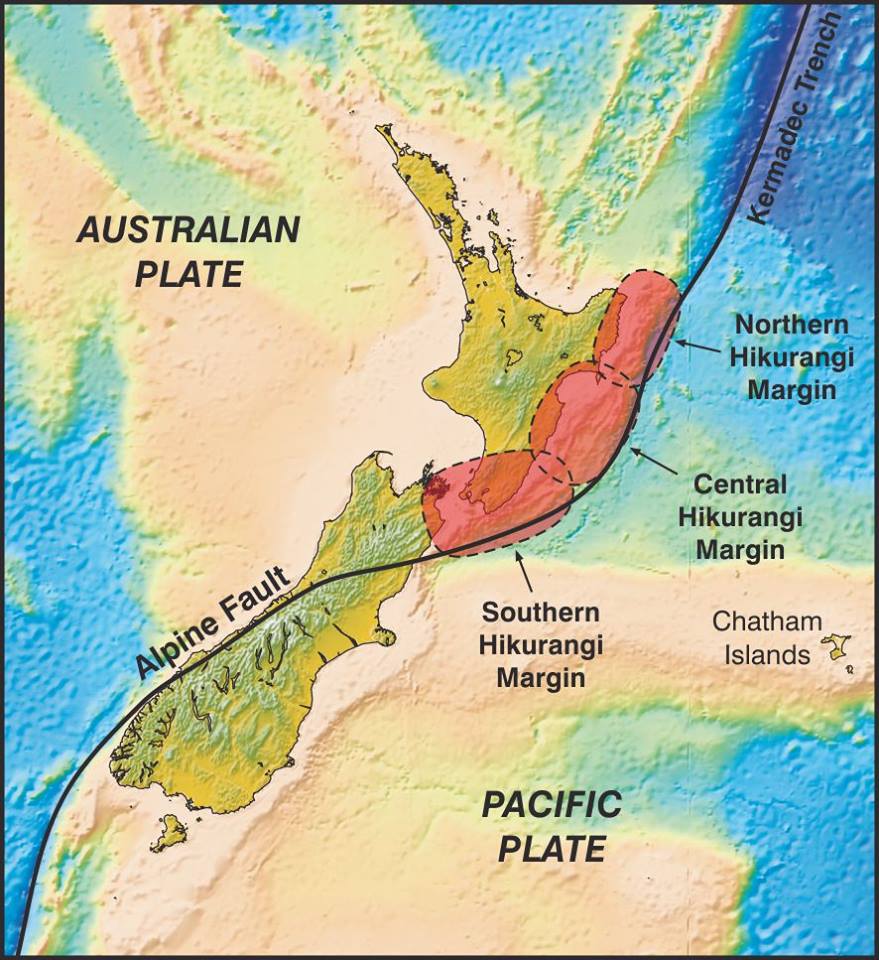
The Pacific and Australian Plates are locked together in the South Island along the Alpine Fault. These two plates are pushing into each other in a transform (right-lateral strikeslip) fault – this is a major 600 km transform fault, which also causes uplift, forming the Southern Alps.

Elastic potential energy builds up over a period of time, and eventually the rock cannot withstand any more strain. This is due to the fault moving \(30mm\) per year. The energy is released as the plates move, releasing a huge amount of energy in an earthquake.
Fault Lines
- Fault lines are cracks in the Earth’s crust often at plate boundaries - but not always
- There are also many smaller fault lines where small movements have occurred.
- E.g. the Malborough fault system
- Earthquakes deep under the North Island tell us exactly where the two plates are rubbing together.
- The melted rock rises up again in volcanic eruptions.
Earthquake Waves
Three types of waves move through Earth’s surface when an earthquake occurs
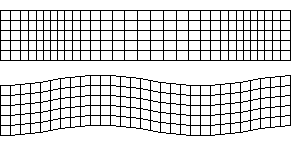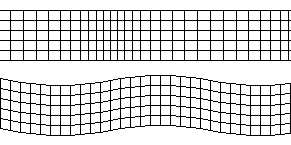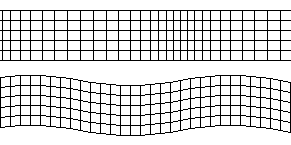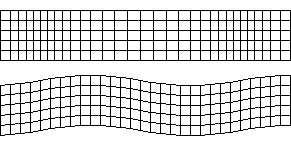
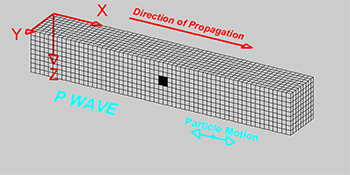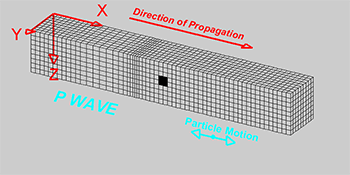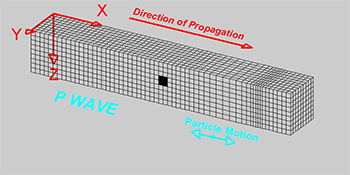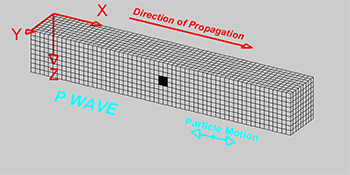
P-Waves
Also known as primary waves are the first waves to hit as they move the fastest (\(8kms^{-1}\)). They squeeze and stretch the rock.
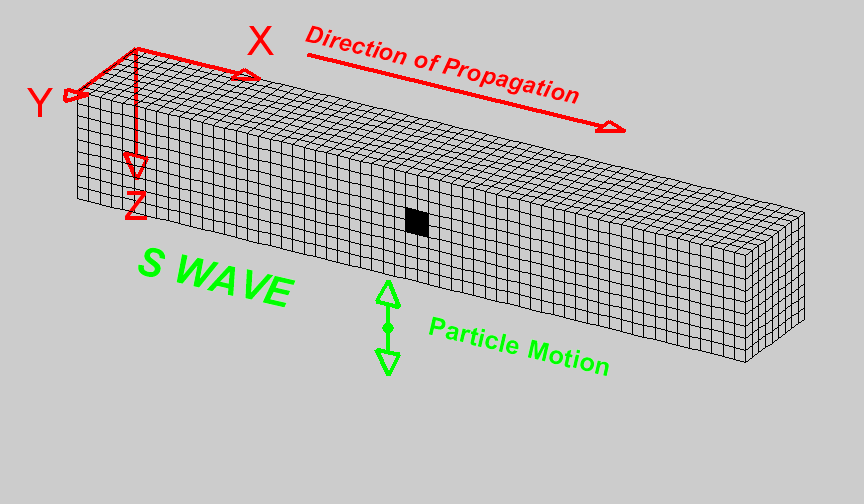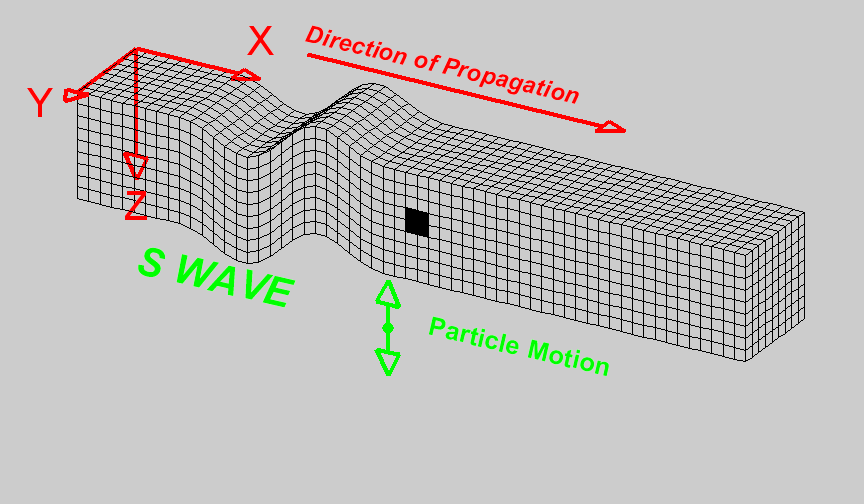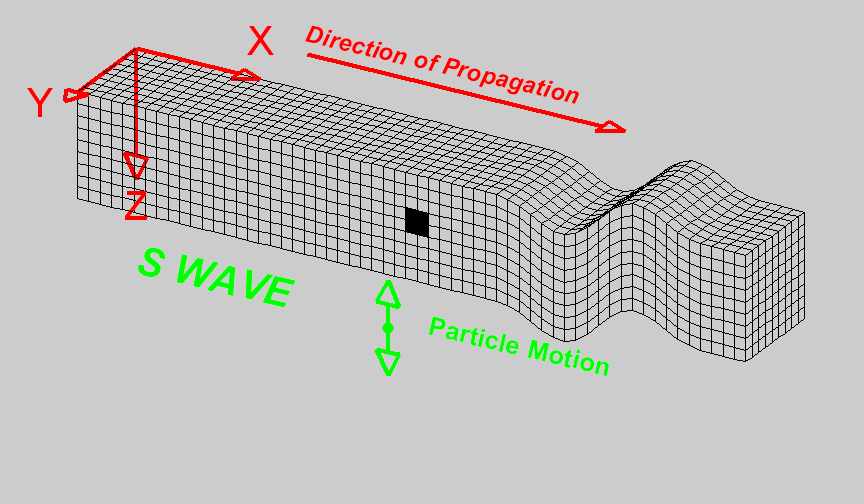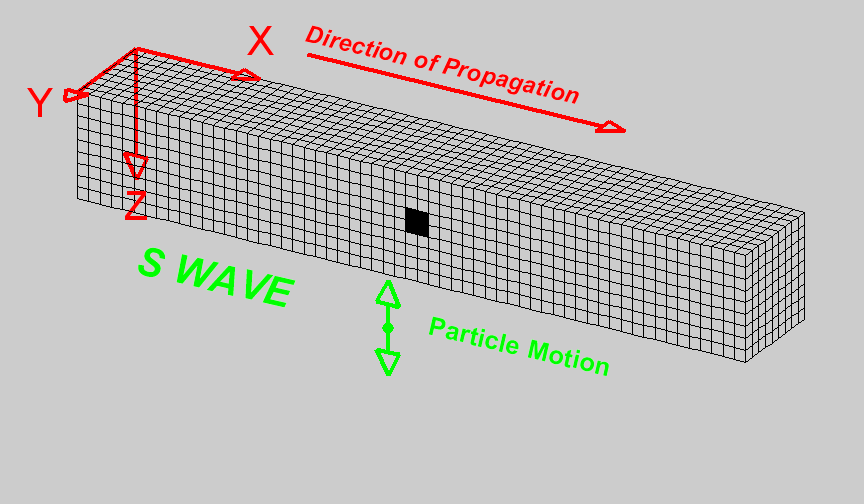
S-Waves
Also known as secondary waves. These waves move at \(5kms^{-1}\) and make the ground shake up and down as well as from side to side.
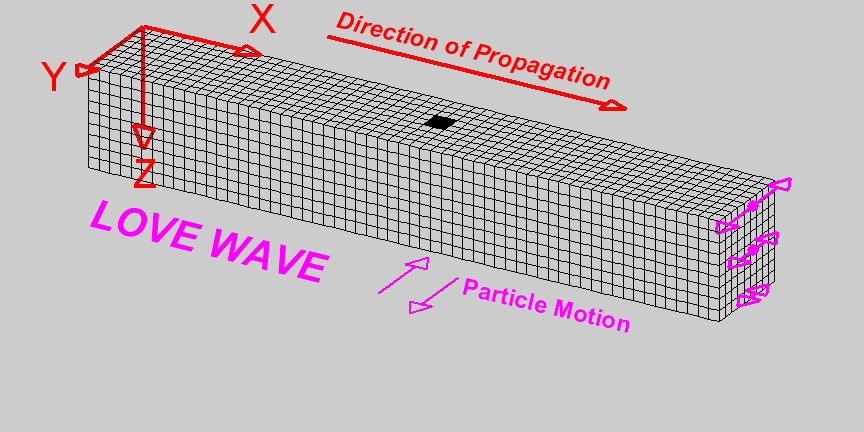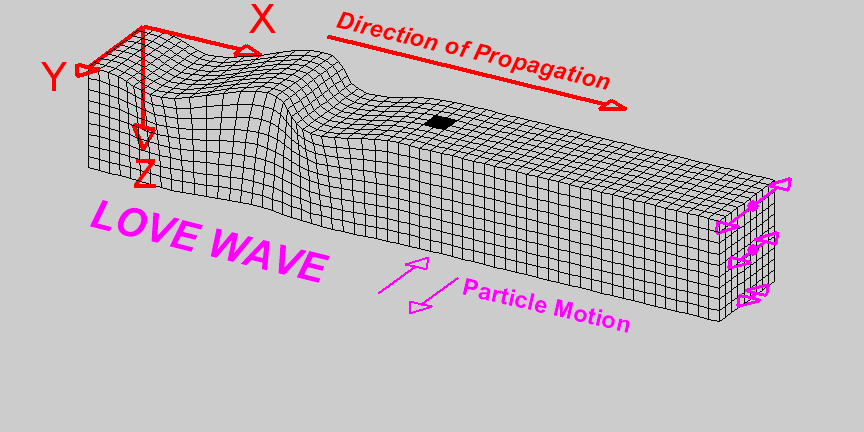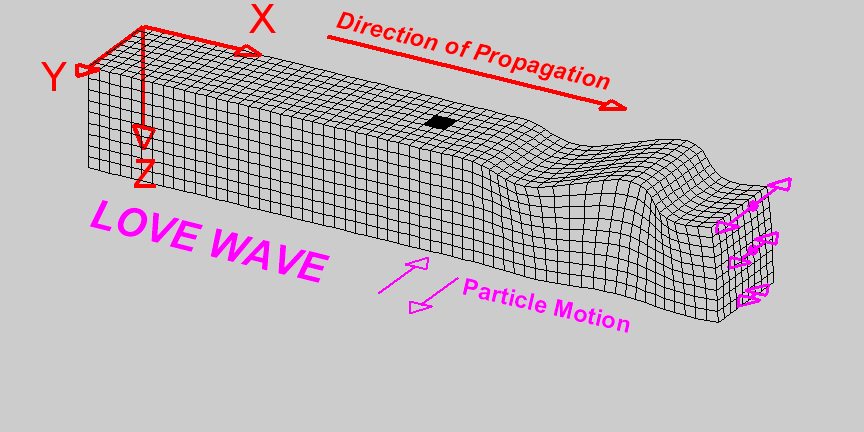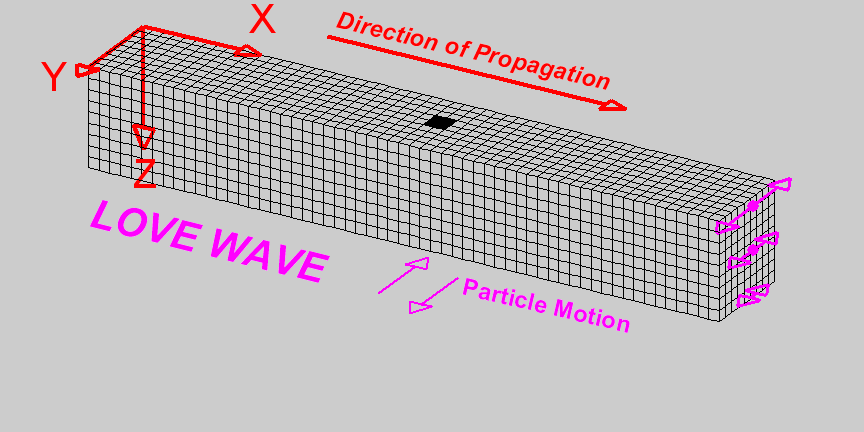
L-Waves
Travelling at \(4kms^{-1}\) are the last waves to hit. These waves do the most damage as they travel near the surface of the crust.
| Features | P- Waves | S - Waves | L - Waves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Primary | Secondary | Long |
| Action | Push / pull | Up / down / sideways | Rolling |
| Travelling Speed | Speed 5 - 13 km/s | Speed 3 - 8 km/s | Speed 3 - 4 km/s |
| Arrival | First | Second | Third |
| Damage Level | Minor | Moderate | Major |
| In Water | Pass through | Absorbed | Pass through |
| Location | In crust | In crust | Surface only |
Measuring Earthquakes
Earthquakes are measured on two different scales:
- The Richter Scale - This measures the amount of energy released in an earthquake, using a seismograph. It is a 10 step scale - each whole number jump has around 32x more energy released
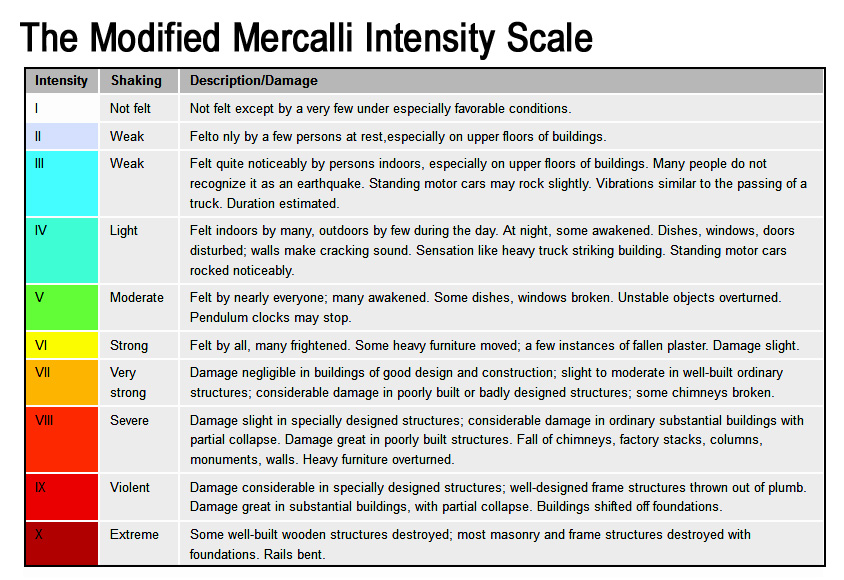
- The Mercalli Scale - This measures the effect on people and the environment at the surface of the quake. It is on a 12 point scale
Mercalli Scale
Earthquake intensity is determined using:
- Strength of earthquake
- Distance from epicenter
- Nature of surface materials
- Building design
The Mercalli scale does not give a true indication of the actual strength of an earthquake because the amount of damage done to different places will largely depend on the type of materials used and the degree of construction of buildings and structures.
Richter Scale
- Measures magnitude of an earthquake on a 10-point scale
- Richter magnitude is determined by measuring the largest amplitude (wave height) recorded on a seismogram.
- Each increase in 1 in Richter Magnitude represents a 30 fold increase in the energy released (size). A magnitude 8 earthquake releases \(30 \times 30 = 900\) times more energy than a magnitude 6 earthquake.



Challenge: Build a Seismograph
Open Google Classroom on your device and find the Build a Seismograph task!