Akoranga 3 Mahi Tuatahi 🔗
- Collect a cloze from the front
- Glue it in
- Fill in the missing words
Mahi Tuatahi Whakatika 🔗
The Earth is composed of 4 main layers - the inner core, outer core, mantle and crust. The outer core is a liquid and extremely hot. The mantle above it is made of semi solid rock. The intense heat from the outer core causes the bottom layer of the mantle to become less dense, and because of this it rises. As the rock gets closer to the crust it cools down and becomes more dense, and begins to sink. This process repeats, resulting in a continuous movement called convection currents. These currents are responsible for the movement of the tectonic plates of the crust above.
Ngā Whāinga Ako 🔗
- Describe the different densities of the crust
- Describe the three types of plate boundaries.
Write the date and ngā whāinga ako in your book
Density 🔗
Mass per unit of volume - so how much stuff is packed into a given space.

Crust Densities 🔗
- Continental crust is made of mostly granite rock, and is less dense than the material of the Earth’s mantle, so it sits on top.
- Oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust. Continental crust makes up about 70% of the volume of Earth’s crust.
- Oceanic crust is thinner, but more dense than continental. This is why at convergent boundaries, the oceanic plate moves underneath the continental.
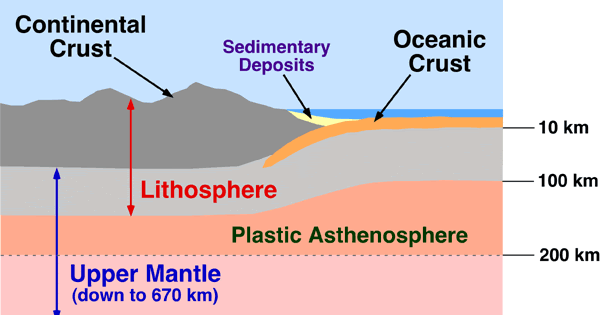
Plate Boundaries 🔗
The area where two tectonic plates meet is called a plate boundary. Mountains, volcanoes and oceanic trenches are formed at plate boundaries, and earthquakes are more likely to occur here.

Types of Plate Boundaries 🔗
Sketch these boundaries into your book.
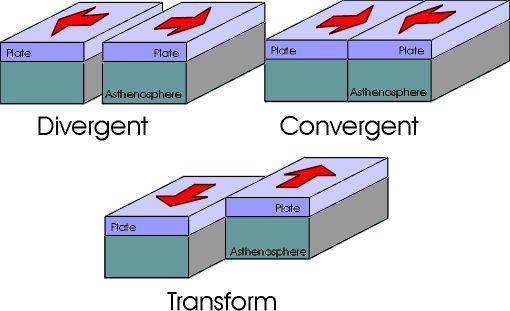
Divergent Boundary 🔗
The plates move away from each other.

- When two plates move away from each other, they create a gap between them. Molten rock (magma) rises from the mantle to fill the gap forming a mid-ocean ridge
- Divergent plate boundaries cause mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes and earthquakes, though they are often less violent than those on convergent plate boundaries.
- Volcanoes can form along the edges of the plate boundary due to the rising magma. These volcanoes are called shield volcanoes.
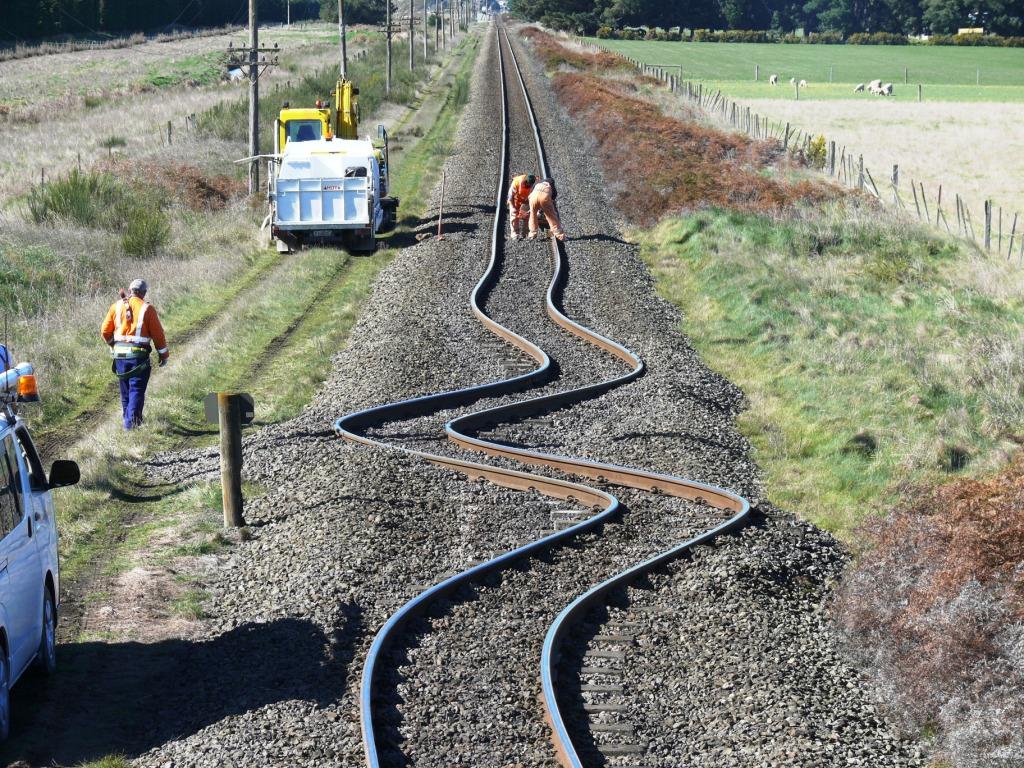
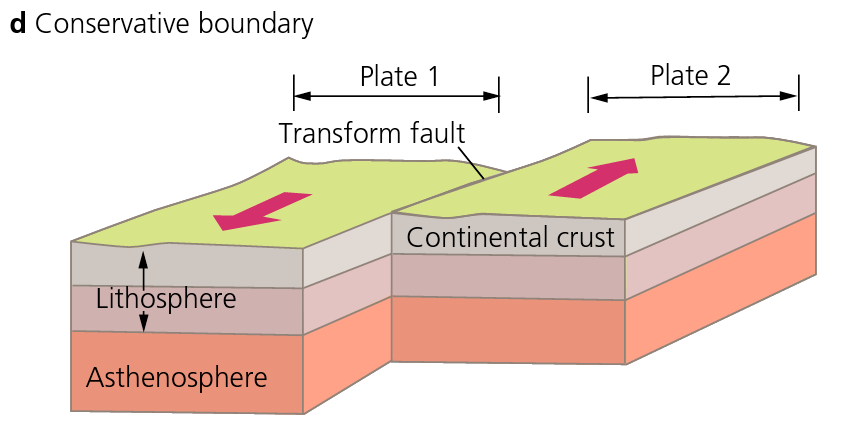
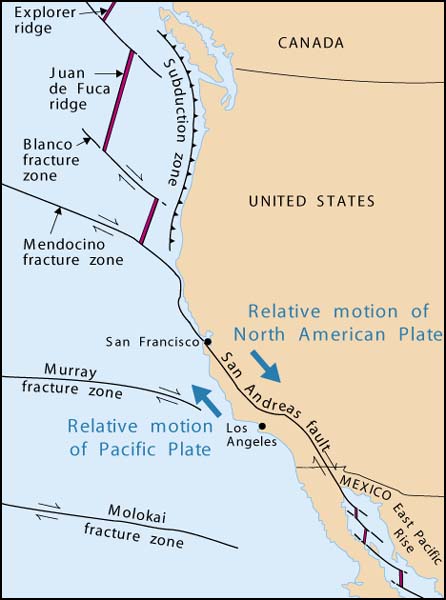
Transform Boundary 🔗
The plates often get stuck as they try to move past each other due to friction. Over time this builds up great pressure until finally they jolt past each other. The sudden movement causes an earthquake which may be violent and cause great damage.



Convergent Boundary 🔗
When two plates move together and collide. Comes in three types.
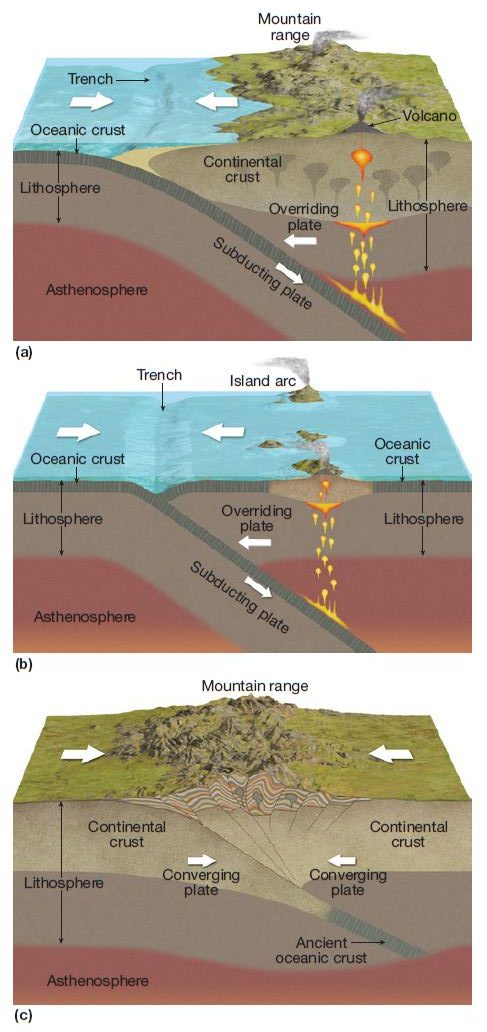
Oceanic-Continental Collision 🔗
The denser oceanic crust subducts under the continental crust, typically making a mountain range/island.

Oceanic-Oceanic Collision 🔗
The denser of the oceanic plates subducts under the other. Sometimes creating magma plumes and creating an island arc system (e.g. Japan), as well as an oceanic trench.

Continental-Continental Collision 🔗
The denser of the continental plates subducts under the other, creating a mountain range.


Task / Ngohe 🔗
- Open Google Classroom and find the Webquest activity.
- Follow the instructions and links to answer the questions!
Whakamātau: Density 🔗
Open Google Classroom to find the Density Investigation