Genetic Crosses
11SCI - Genetics
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Ngā Whāinga Ako
- Understand and use the terms “genotype and phenotype”, “homozygous and heterozygous” and “dominant and recessive”.
- Know how to carry out genetic crosses using punnet squares and determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
Some Definitions
- Genotype: The genetic make-up of a cell that determines one of its characteristics
- Phenotype: The observable characteristics of an individual due to its genotype
Phenotype
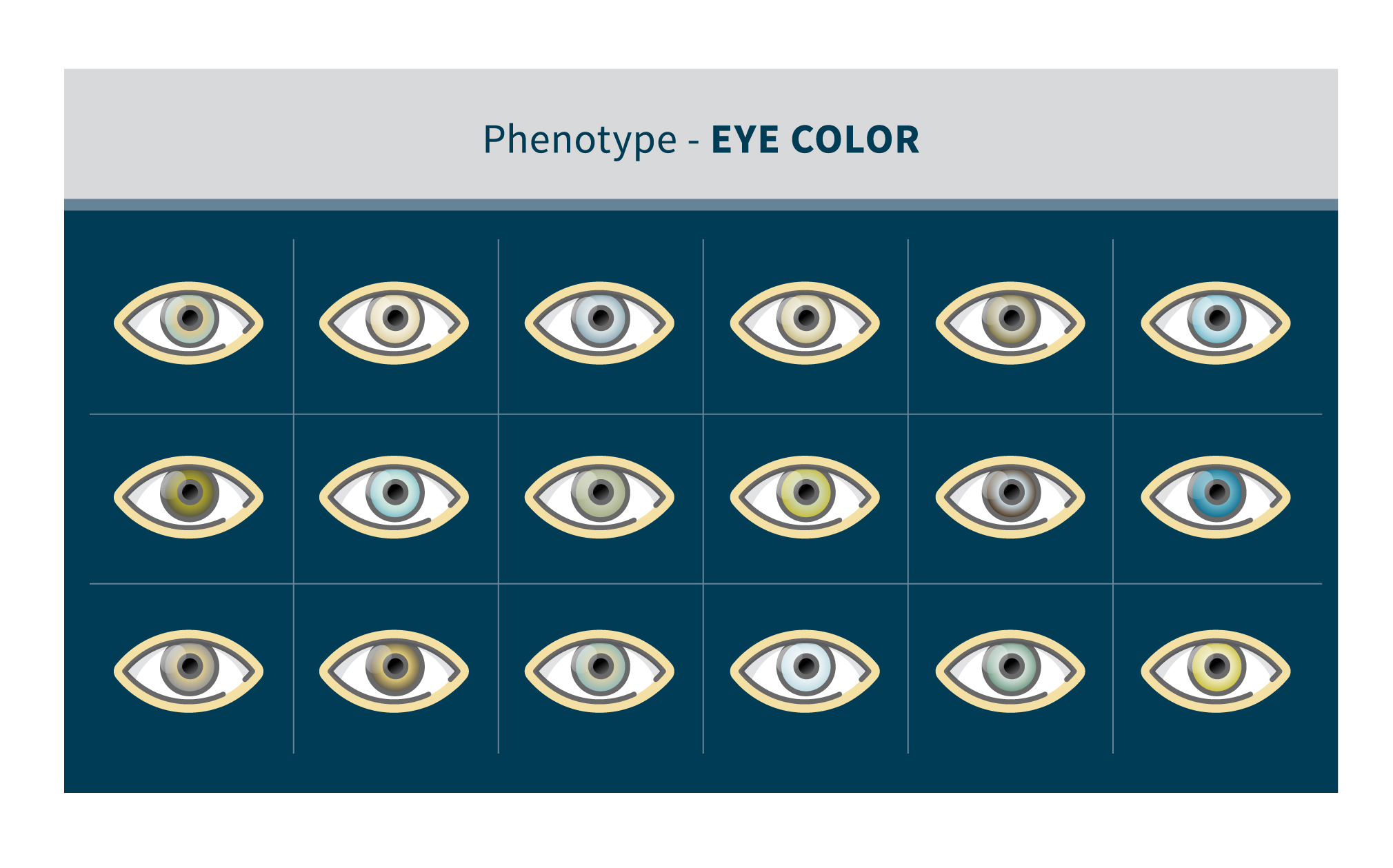
Genotype
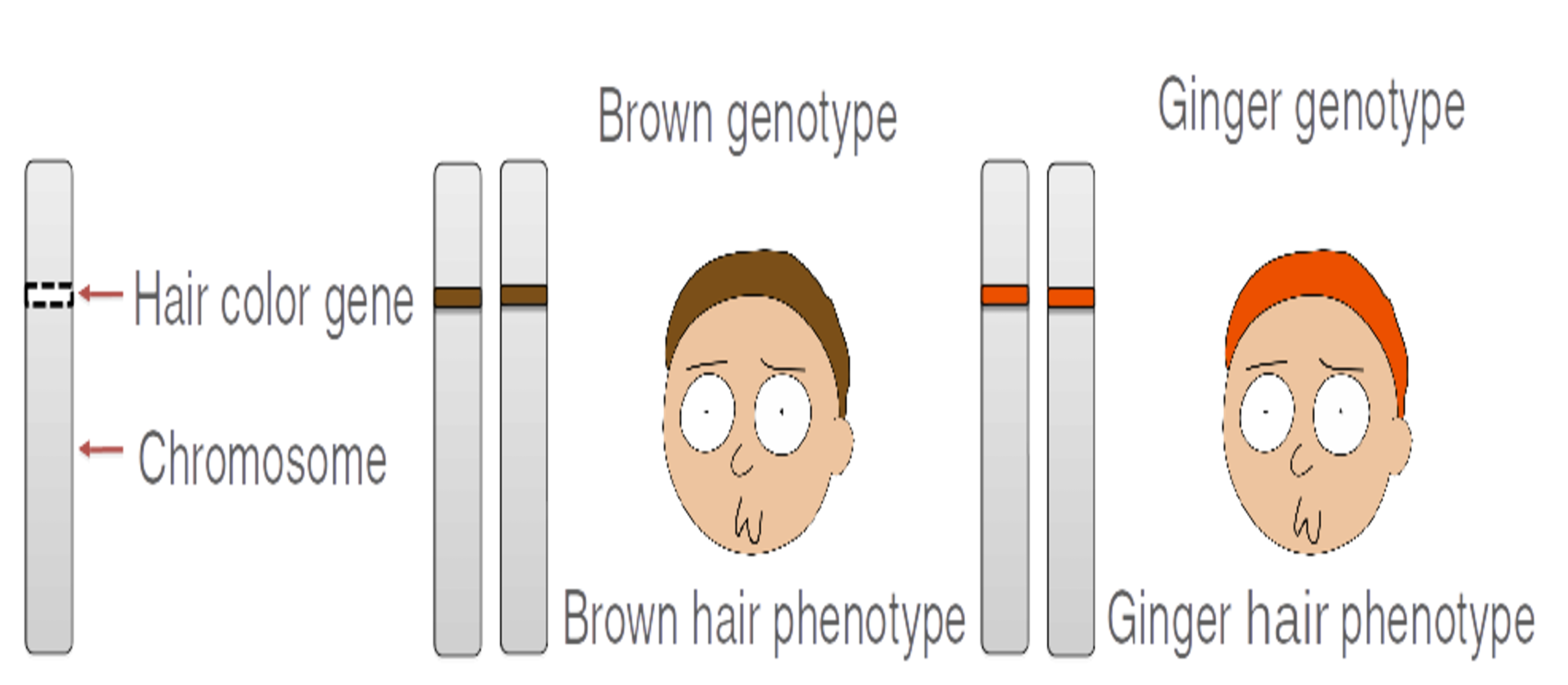
How do we describe the genotype?
- We use the words dominant and recessive to describe alleles.
- What is an allele?
Dominant Alleles
- A dominant allele will produce a certain phenotype, even in the presence of other alleles.
- For example, a brown eyes allele will create brown eyes even when paired with a blue eyes allele.
- If B is brown and b is blue: BB and Bb will both produce brown eyes.
Recessive Alleles
- A recessive allele will only produce a certain phenotype when in the presence of another of the same allele.
- For example, a blue eyes allele will only create blue eyes when paired with another blue eyes allele.
- If B is brown and b is blue: BB and Bb will both produce brown eyes, while only bb will produce blue.
- Recall homo means same and hetero means different
- BB is homozygous dominant
- Bb is heterozygous dominant
- bb is homozygous recessive
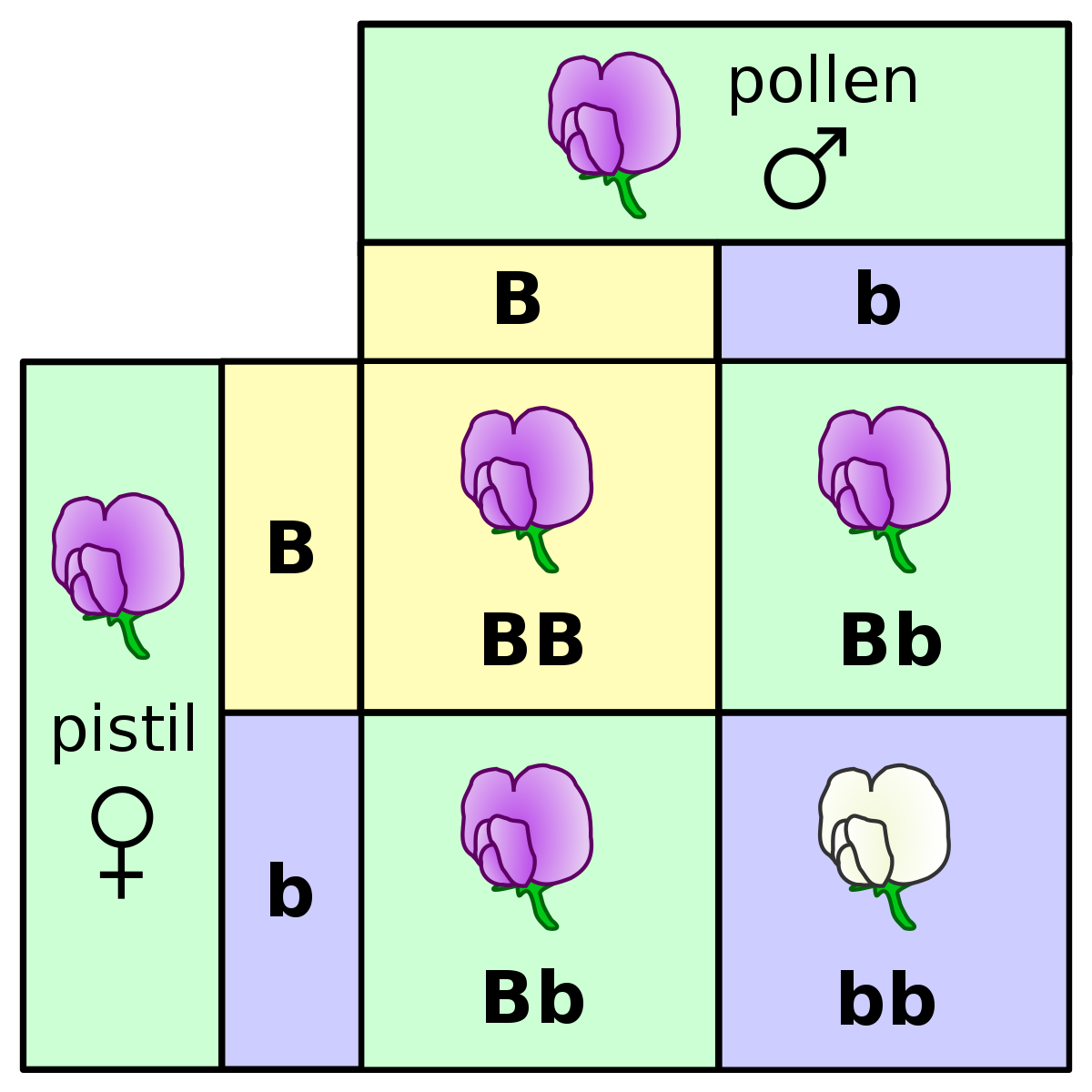
Punnet Squares
- We can use punnet squares to determine the probability that two parents will produce offspring with a particular genotype, or with a particular phenotype.
- The father goes at the top of the square, and the mother on the left.
- We fill out the known genotypes of the parents and then complete the square.
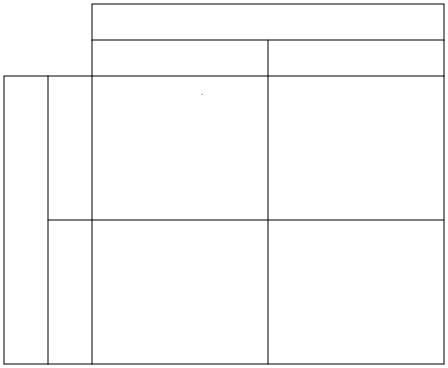
If dad is heterozygous dominant for brown eyes and mum is homozygous recessive for blue eyes, complete this punnet square in your books.
Test Crosses
A test cross used to determine the genotype of an unknown organism. It is done by crossing the organism with an organism that is known to be homozygous recessive.
The Two Outcomes
There are two possible outcomes for a test cross.
- The organism is homozygous dominant,
- the organism is heterozygous.
Question
A garden pea has two alleles for colour. Y is the dominant allele for yellow, while y is the recessive allele for green.
Mendel wants to figure out whether his yellow pea is homozygous dominant or heterozygous. How can he do this?
Answer
He can breed the pea plants together many times and count the number of yellow and green pea plants produced. He can also perform two punnet squares to figure out which genotype the yellow pea has e.g. YY x yy and Yy x yy.