Chromosomal Disorders
11SCI - Genetics
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Chromosomal Disorders / Abnormalities
- Occur when there is an atypical number of chromosomes
- Occur if a chromosome is structurally changed
- Occur if large parts of a chromosome are altered
- Typically occur during mitosis (feotal development) or meiosis (production of gametes).
Trisomy 21
- Occurs when there is a third copy of chromosome 21
- Results in down syndrome
- 1 in 1,600 to women age 20

Turner Syndrome
Occurs when one of the two X chromosomes in females is either missing or incomplete. The most common symptoms are short stature and gonadal dysgenesis (abnormal development of gonads), which can cause incomplete sexual development and ovarian failure and infertility. 1 in 2000-2500 live births.

Triple-X Syndrome
Characterized by an extra X chromosome in each of a female’s cells. It does not cause any unusual physical features but is associated with the increased risk of learning disabilities and delayed development of speech and language skills. 1 in 1000.

Trisomy 18/Edwards syndrome
Occurs when a person has a third copy of material from chromosome 18 instead of the usual two copies. Some symptoms include clenched hands, feet with a rounded bottom, mental deficiency, underdeveloped fingernails, and an unusual shaped chest. 3 in 10,000.
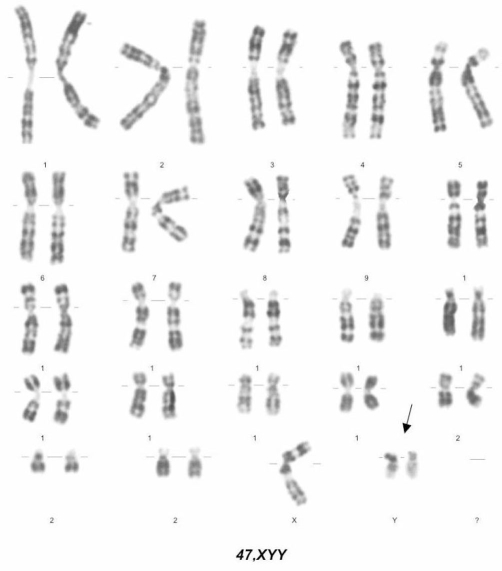
Klinefelter Syndrome
When a male has an additional copy of the X chromosome (XXY). Results in infertility, small and poorly functioning testicles, possibly weaker muscles, greater height, poor motor coordination, less body hair and breast growth. 2 in 10,000.
Trisomy 16
Occurs when an individual has three copies of chromosome 16 instead of the usual two and is the most common chromosomal cause of miscarriage during the pregnancy’s first trimester.

Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome
Caused by the deletion of the distal short arm of chromosome 4. The disorder’s major features include a characteristic facial appearance, delayed growth and development, intellectual disability, and seizures.

Jacob’s Syndrome
Caused by an extra copy of the Y chromosome in males (XYY). Leads to increased height, acne, increased risk of learning disabilities. They are typical in most other ways.