Atoms
pHun Reactions - 10SCIE
Finn Le Sueur
2024
What is pHun Reactions?
- A unit about chemical reactions, atoms and ions!
- We will learn about atomic structure,
- ions,
- ionic compounds,
- acids and bases,
- and neutralisation reactions!
Glue in your learning outcomes sheet!
Ngā Whāinga Ako
- Use diagrams to represent the arrangement of protons, neutrons and electrons in atoms.
- Use the periodic table to find proton, neutron and electron numbers.
Write the date and ngā whāinga ako in your book
Atoms
- To understand chemistry, we need to first start by learning about atoms and their structure!
- Atoms have three sub-atomic particles:
- Protons
- Electrons
- Neutrons
- Pātai: With the person next to you, draw a diagram of an atom in your book (if you can!).
- Protons
- Exist in the nucleus of the atom
- Have a positive charge
- Electrons
- Exist in shells/orbitals around the nucleus
- Have a negative charge
- Neutrons
- Exist in the nucleus of the atom
- Have no charge (neutral)

- In a neutral atom/element there is the same number of protons and electrons
- The number of protons determines what element the atom is
- The atomic number is also known as the mass number

Glue in your periodic table at the front/back of your book so you can always find it!
Elements
- Which elements do you need to know?
- The first 20!
- From hydrogen to calcium!
- Open the link on Classroom and start practising!
Akoranga 2 Mahi Tuatahi
- Open to the back of your book
- Answer these questions without looking at your notes!
- Copy this diagram and fill in the missing labels
- What element is this?
- What is the symbol of this element?
- How many protons exist in the nucleus of this atom?
- How many electrons exist in the shells?

- What element has symbol K?
- What element has symbol Be?
- What is the symbol of aluminium?
- What is the symbol of argon?
- How many protons does carbon have?
Ngā Whāinga Ako
- Can use the periodic table to find proton, neutron & electron numbers
- Can define atomic and mass number
Write the date and ngā whāinga ako in your book
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. Each element has a different number of protons.

Mass Number
The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Your periodic table gives an average mass number. You should round it to the nearest whole number.

Pātai: Sodium
- How many protons does sodium have in its nucleus?
- How many neutrons does sodium have in its nucleus?
- How many electrons orbit around sodium?
- Why is there that many electrons?

Whakatika
- How many protons does sodium have in its
nucleus?
11 - How many neutrons does sodium have in its
nucleus?
\(23-11=12\) - How many electrons orbit around
sodium?
11 - Why is there that many
electrons?
Because the number of protons and electrons are the same in neutral atoms.

Pātai: Phosphorous
- How many protons does phosphorous have in its nucleus?
- How many neutrons does phosphorous have in its nucleus?
- How many electrons orbit around phosphorous?
- Why is there that many electrons?
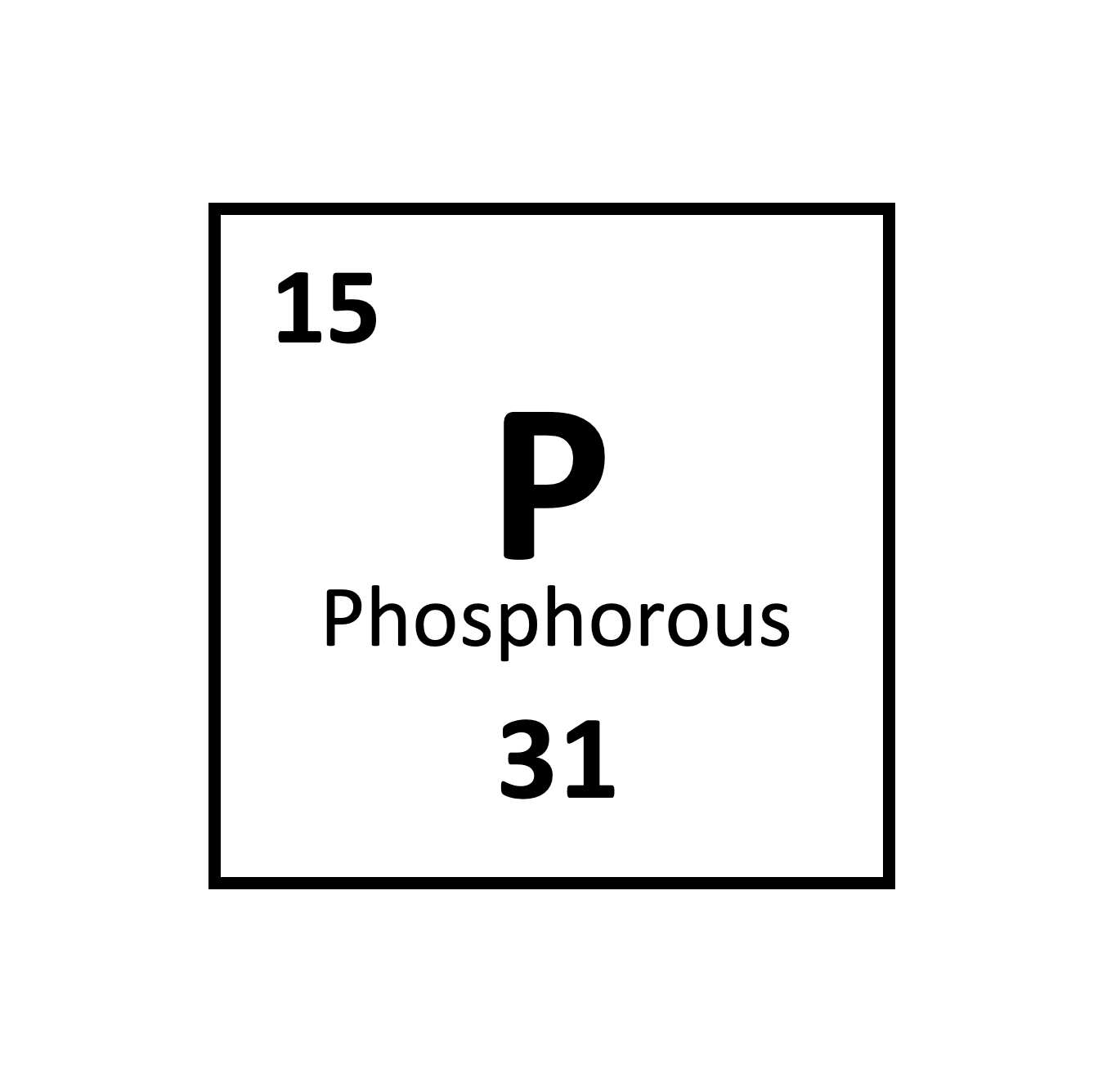
Whakatika
- How many protons does phosphorous have in
its nucleus?
15 - How many neutrons does phosphorous have in
its nucleus?
\(31-15=16\) - How many electrons orbit around
phosphorous?
15 - Why is there that many
electrons?
Because the number of protons and electrons are the same in neutral atoms.

Tākaro/Game: Atom Battleships
- Collect a board from the front
- Pair up
- Follow the instructions on the board!
Ngohe/Task: Atoms
- Collect a sheet from the front of class
- Glue it into your book
- Put any extra un-crumpled paper into the green bin
- Use your periodic table to fill out the sheet
- Do not complete the last three columns!