Static Electricity
Electricity - 10SCIE
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Akoranga 1 Mahi Tuatahi
- Collect a whiteboard from the front
- In pairs, brainstorm things you think you know about electricity
- Anything at all!
- Title a new page ELECTRICITY
- Glue in the learning outcomes/ngā whāinga ako sheet
- Write the date in your book
- Write the learning outcome for today:
- Explain how static electricity is created by the removal or addition of electric charge.
Electricity as a Job
Electricity for Fun
Electricity as Danger
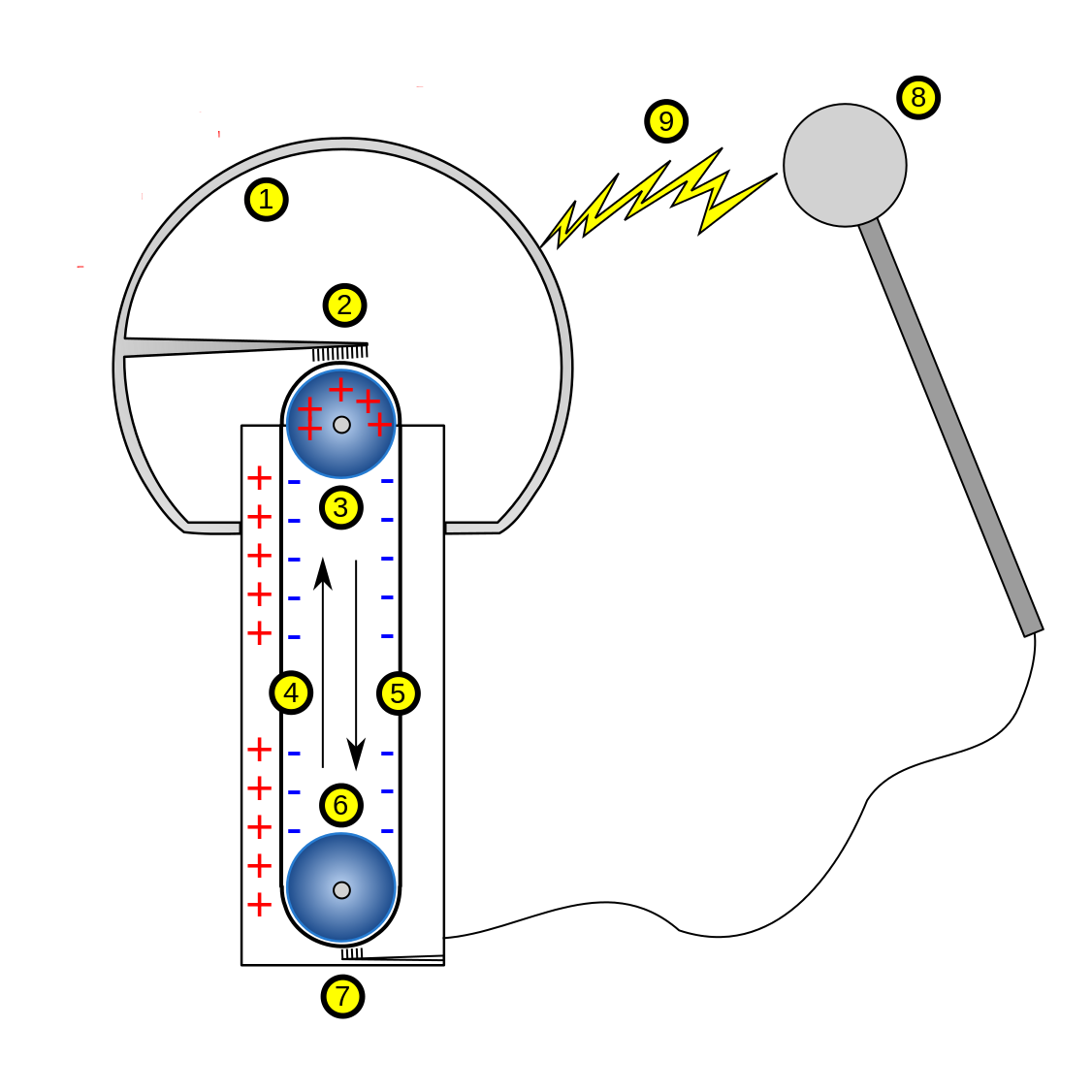
Van der Graaf Generator

- The dome builds up a charge, and this can be used to do all kinds of interesting things
- The wand is used to complete the circuit and to stop charge building up
- Key: Opposites attract and likes repel
Tinfoil Pie Containers
- Pātai: Why do they not fly off straight away?
- Whakatika: Because the circuit is complete; no charge building up.
- Pātai: What will happen when the circuit is broken?
- Whakatika: Positive charge begins to build up on the dome, so the tinfoil pie contains repel each other.

Lightning
- Pātai: What is happening when the circuit is not complete?
- Whakatika: Charge is building up in the dome
- Pātai: Why does lightning occur?
- Whakatika: Because the charges want to balance out.

Van der Graaf Generator Explained
Akoranga 2 Mahi Tuatahi
- Collect a whiteboard from the front
- In pairs, draw and label a diagram of an atom!
Te Whāinga Ako
- Explain how static electricity is created by the removal or addition of electric charge.
Write the date and te whāinga ako in your book
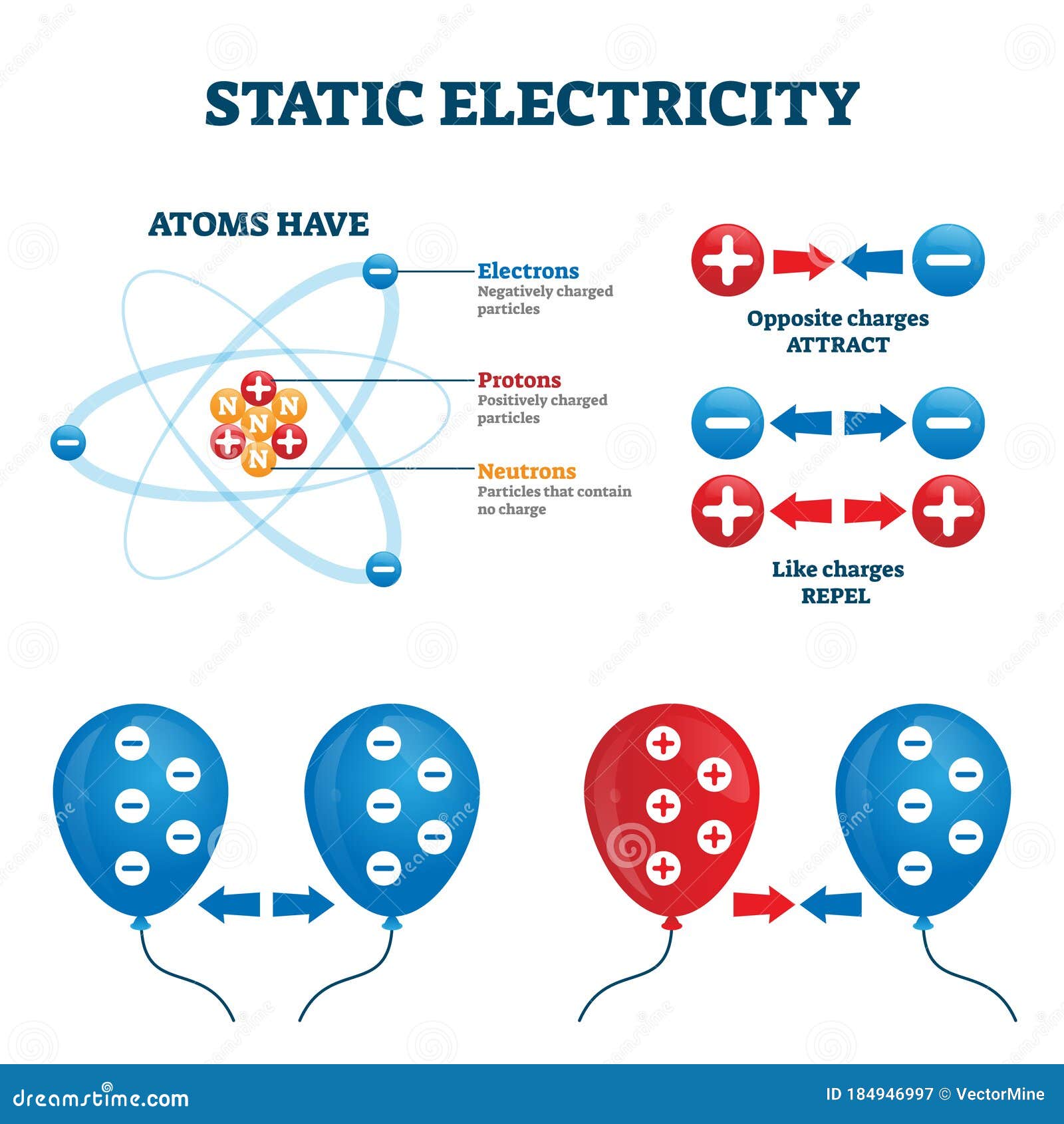
Atomic Structure
- Nucleus: The centre of the atom (strongly held: protons, neutrons)
- Orbit: Loosely held electrons orbit around the nucleus

Removing/Adding Charge
- The nucleus is strongly held and is positively charged because it contains protons which have a positive charge.
- Neutrons have no charge (neutral)
- The electrons are loosely held, and are negatively charged.
- Electrons can be removed from a material via friction


Pātai: Why can’t protons (positive charge) be removed?
Discuss with the person next to you!
Whakatika
- Protons are in the nucleus which is strongly held
- The nucleus is the core of what makes up matter
- Therefore, we can more easily remove the loosely held electrons
- To remove the protons is to change what the matter is

Static Electricity
An imbalance of charge on the surface of, or inside a material. Imbalances in charge will always attempt to balance out (become neutral), by having charges move.

Electrostatic Induction
- Bringing a charged object near a neutral one can induce a localised opposite charge. Therefore, creating attraction between the two objects
- Make a note of this diagram and notes in your book.
- Explain how you can use an electroscope to determine whether an object is charged or not.
