Series and Parallel Circuits
Electricity - 10SCIE
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Ngā Whāinga Ako
- Construct series and parallel circuits
- Measure and explain the behaviour of voltage, current and resistance in series and parallel circuits
Write the date and ngā whāinga ako in your book

Series Circuits
The current has only one path to flow around
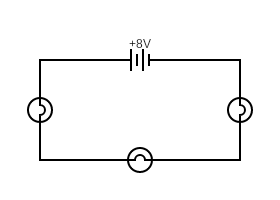
The current is the same all around the circuit
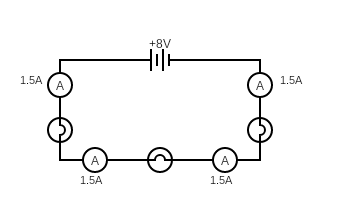
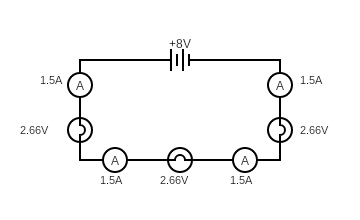
- The voltage is shared (equally) between the components in the loop if they have the same resistance
- All the components voltage adds to the voltage of the power supply
- All of the voltage must be consumed
Copy this diagram into your book.
Ngohe/Task
- Collect a sheet from the front
- Cut it to size and glue it into your book
- Work in pairs to complete the Series side of the sheet
Tūhura/Investigation
- Collect a electricity tray.
- Build the circuit on the right.
- Set the voltage to \(12V\).
- Add a second bulb to the circuit.
- Write down your observation and explanation in your book!
- Pack up your electricity tray and return it to the trolley.
Parallel Circuit
The current has multiple paths to flow around
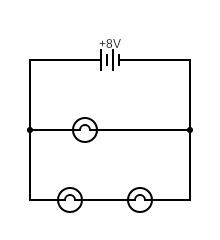
The current is shared between paths
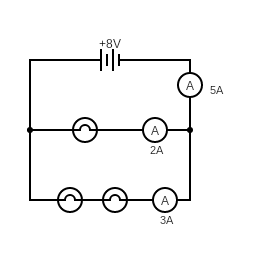
- The voltage is shared between components on each separate path
- Each path voltage adds to the voltage of the power supply
Copy this diagram into your book.
Ngohe/Task
Work in pairs to complete the Parallel side of the sheet you collected earlier.
Tūhura/Investigation
- Collect a electricity tray.
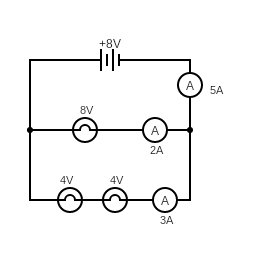
- Copy this diagram into your book.
- Build the circuit on the right and set \(V=12V\) (measure with your multimeter too).
- Use a multimeter to measure the unknown voltages.
- Move the ammeter to measure the current at the unknown points.
- Pack up your electricity tray and return it to the trolley.