Resistance
Electricity - 10SCIE
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Te Whāinga Ako
- Describe how resistance controls the flow of electric current
Write the date and te whāinga ako in your book
Resistance
- Resistance is a measure of how difficult it is for charges (electrons) to flow through a circuit component
- A higher resistance ➡ lower current
- A lower resistance ➡ higher current
- It is letter \(R\) in equations
- It has the unit Ohm, given the Greek letter capital Omega: \(\Omega\)
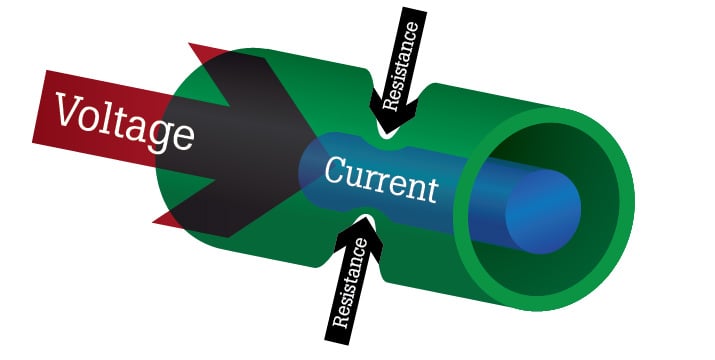
- You can think of it as a skinny pipe which cannot carry as much water as a larger pipe
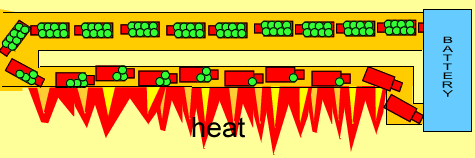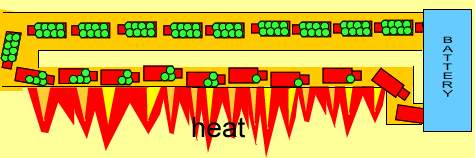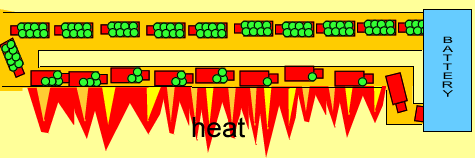
- When electrons move through a material with resistance, they lose some energy in the form of heat (and light, when hot enough)
- E.g. your toaster, filament lightbulbs, hair dryer, heater, hair straightener
- Materials with very high resistance are called insulators
- Materials with very low resistance are called conductors
The amount of resistance in a component is related directly to the voltage and current flowing through it. This equation is known as Ohm’s Law.
\[\begin{aligned} &V &&= &&&I &&&&\times &&&&&R \newline &\downarrow && &&&\downarrow &&&& &&&&&\downarrow \newline &voltage &&= &&¤t &&&&\times &&&&&resistance \newline &\downarrow && &&&\downarrow &&&& &&&&&\downarrow \newline &volts &&= &&&eres &&&&\times &&&&&ohms \newline &\downarrow && &&&\downarrow &&&& &&&&&\downarrow \newline &V && &&&A &&&& &&&&&\Omega \end{aligned}\]Pātai Tahi
An current of \(1A\) flows through a resistor with resistance \(2\Omega\). Calculate the voltage consumed by the resistor.
\[\begin{aligned} &\text{(Knowns)} \newline &\text{(Unknowns)} \newline &\text{(Formula)} \newline &\text{(Substitute + Solve)} \end{aligned}\]Whakatika
\[\begin{aligned} & I = 1A, R = 2\Omega && \text{(K)} \newline & V = ? && \text{(U)} \newline & V = IR && \text{(F)} \newline & V = 1 \times 2 = 2V && \text{(S+S)} \end{aligned}\]Pātai Rua
An current of \(0.01A\) flows through a resistor with resistance \(1000\Omega\). Calculate the voltage consumed by the resistor.
\[\begin{aligned} &\text{(Knowns)} \newline &\text{(Unknowns)} \newline &\text{(Formula)} \newline &\text{(Substitute + Solve)} \end{aligned}\]Whakatika
\[\begin{aligned} & I = 0.01A, R = 1000\Omega &&\text{(K)} \newline & V = ? &&\text{(U)} \newline & V = IR &&\text{(F)} \newline & V = 0.01 \times 1000 = 10V &&\text{(S+S)} \end{aligned}\]Pātai Toru
An current of \(0.01A\) flows through a resistor with resistance \(50000\Omega\). Calculate the voltage consumed by the resistor.
\[\begin{aligned} &\text{(Knowns)} \newline &\text{(Unknowns)} \newline &\text{(Formula)} \newline &\text{(Substitute + Solve)} \end{aligned}\]Whakatika
\[\begin{aligned} & I = 0.01A, R = 50000\Omega && \text{(K)} \newline & V = ? && \text{(U)} \newline & V = IR && \text{(F)} \newline & V = 0.01 \times 50000 = 5000V && \text{(S+S)} \end{aligned}\]Pātai Whā
An current of \(0.01A\) flows through a \(6V\) bulb. Calculate the resistance of the bulb.
\[\begin{aligned} &\text{(Knowns)} \newline &\text{(Unknowns)} \newline &\text{(Formula)} \newline &\text{(Substitute + Solve)} \end{aligned}\]Whakatika
\[\begin{aligned} & I = 0.01A, V = 6V && \text{(K)} \newline & R = ? && \text{(U)} \newline & V = IR && \text{(F)} \newline & 6 = 0.01 \times R \text{(S+S)} \newline & \frac{6}{0.01} = R = 600\Omega \end{aligned}\]Pātai Rimu
Calculate the current that flows through a \(10V\) bulb with a resistance of \(400\Omega\).
\[\begin{aligned} &\text{(Knowns)} \newline &\text{(Unknowns)} \newline &\text{(Formula)} \newline &\text{(Substitute + Solve)} \end{aligned}\]Whakatika
\[\begin{aligned} & V = 10V, R = 400\Omega && \text{(K)} \newline & I = ? && \text{(U)} \newline & V = IR && \text{(F)} \newline & 10 = I \times 400 && \text{(S+S)} \newline & \frac{10}{400} = I = 0.025A \end{aligned}\]Tūhura/Investigation: Ohm’s Law
- Open the PhET Simulation on Google Classroom.
- The voltage and resistance sliders allow you to change those properties of the circuit.
- What impact does increasing the voltage have on the circuit? Extra: Why?
- What impact does increasing the resistance have on the circuit? Extra: Why?
Whakatika
- What impact does increasing the voltage
have on the circuit? Extra: Why?
Increasing the voltage increases the current in the circuit. Because a higher “pressure” is exerted by the power source, causing more electrons to flow around the circuit. - What impact does increasing the resistance
have on the circuit? Extra: Why?
Increasing the resistance decreases the current in the circuit. Because there is more friction acting upon the electrons, stopping them from flowing as freely.