Akoranga 3 Mahi Tuatahi 🔗
Stella shuffles around her house wearing a pair of wool socks. She wants to shock one of her friends.
- Explain why she has to shuffle around the floor
- Explain why a shock will be produced
Whakatika / Answer 🔗
- Explain why she has to shuffle around the floor
This applies friction between the socks and the floor. This will remove electrons (negative charge) from the socks, leaving them positively charged. - Explain why a shock will be produced
When there is an imbalance in charge (static electricity), the charges will want to balance out and become neutral. This often occurs as an electric shock.
Electrical Diagrams 🔗
- A big part of Electricity is being able to draw and label diagrams. This helps us understand questions and is a key skill for the test.
- We need to learn a series of common symbols that get used in diagrams.

Symbols, Names and Uses 🔗
In your book, draw the symbol, write the name and the use (if applicable).
Wires: A straight line with right-angled corners that connects electrical components
Open Switch 🔗
A break in the circuit - stops the current from flowing.

Closed Switch 🔗
Makes the circuit complete - allows the current to flow.

Ammeter 🔗
Measures the flow of current in the circuit. Placed in the circuit in series.

Voltmeter 🔗
Measures the amount of voltage used up by components in the circuit. Placed in the circuit in parallel.

Battery 🔗
Provides energy to the circuit.

Cell 🔗
Provides energy to the circuit.

Diode 🔗
Only lets the current flow in one direction (the direction of the arrow).

Fuse 🔗
Heats up and breaks when the current gets too high. Protects the circuit from electrical fires.

Lamp 🔗
Creates light by using up energy.

Motor 🔗
Uses energy to create rotational motion.

Resistor 🔗
Reduces the current in the circuit by impeding flow of electrons.

Variable Resistor 🔗
A resistor that can be changed to reduce the current more or less.

Connecting Components in Series 🔗
Connecting in series means to put them in the same loop.
- The resistor and ammeter are in series because they are in the same loop.
- Always place an ammeter in series. Placing it in parallel will break it.
Connecting Components in Parallel 🔗
Parallel components exist on separate loops of the circuit.
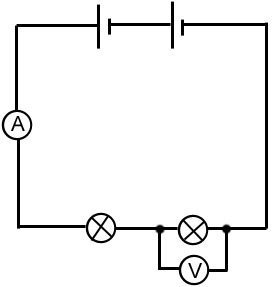
- The light bulbs and ammeter are in series, but the voltmeter is in parallel.
- Always place a voltmeter in parallel because it measures the “different” in voltage between two points.
Pātai 🔗
- Neatly draw these circuits in your book.
- In pairs, decide whether each circuit is a parallel or series circuit.

Whakawai / Practise: Drawing Circuits 🔗
- A circuit with a battery, two bulbs in series.
- A circuit with a battery, two bulbs, an open switch and a resistor in series.
- A circuit with a battery, two bulbs in parallel, with a switch that can turn both lights on/off.
- A circuit with a battery, two bulbs in parallel, with a switch that can turn one bulb on/off.
- A circuit with a battery, three bulbs and a switch, where two bulbs can be controlled by the switch, and the third is always on.