Micro-Organisms
10SCIE - Ecology
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Akoranga 7 Mahi Tuatahi
- Get our your laptop or phone
- Get open www.kahoot.it
https://create.kahoot.it/details/food-web-food-chain/0b1082af-894b-4b54-9893-bd56ff55d9c4
Te Whāinga Ako
- Describe the structure of bacteria and Fungi, labelling the important structures
Write the date and te whāinga ako in your book
Micro-Organisms

- Micro-organisms/microbes are too small to see with the naked eye
- They are either unicellular (made of one cell), or a small group of cells
- Two main categories: bacteria and fungi
Bacteria

- Single celled organism (unicellular)
- Typically a few micrometers in size (\(0.000001m\))
- Come in many different shapes (e.g. spirals, rods, spheres)
Structure of Bacteria
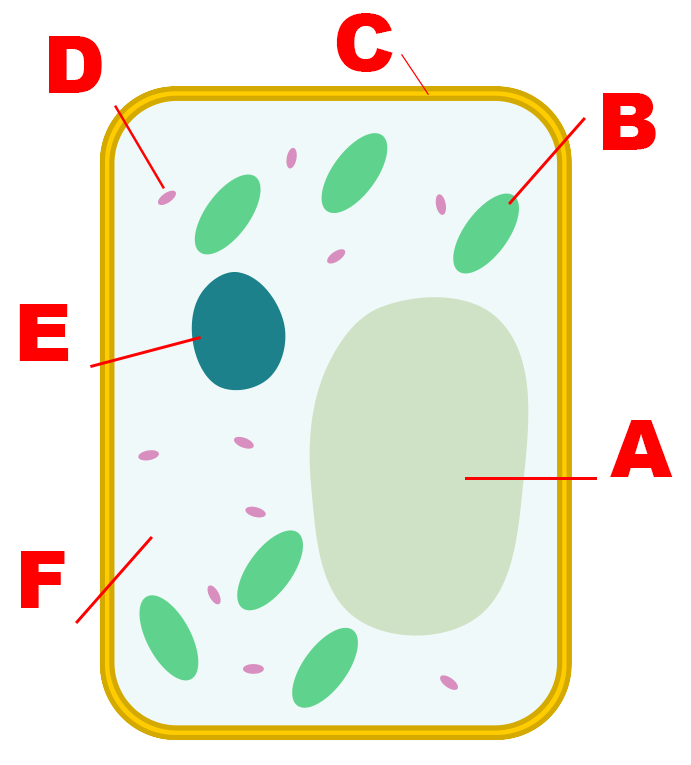
- Stick in your unlabelled bacteria diagram
- Label these structures!
- Vacuole
- Nucleus
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria
- Lipid globules
Fungi (Decomposers)
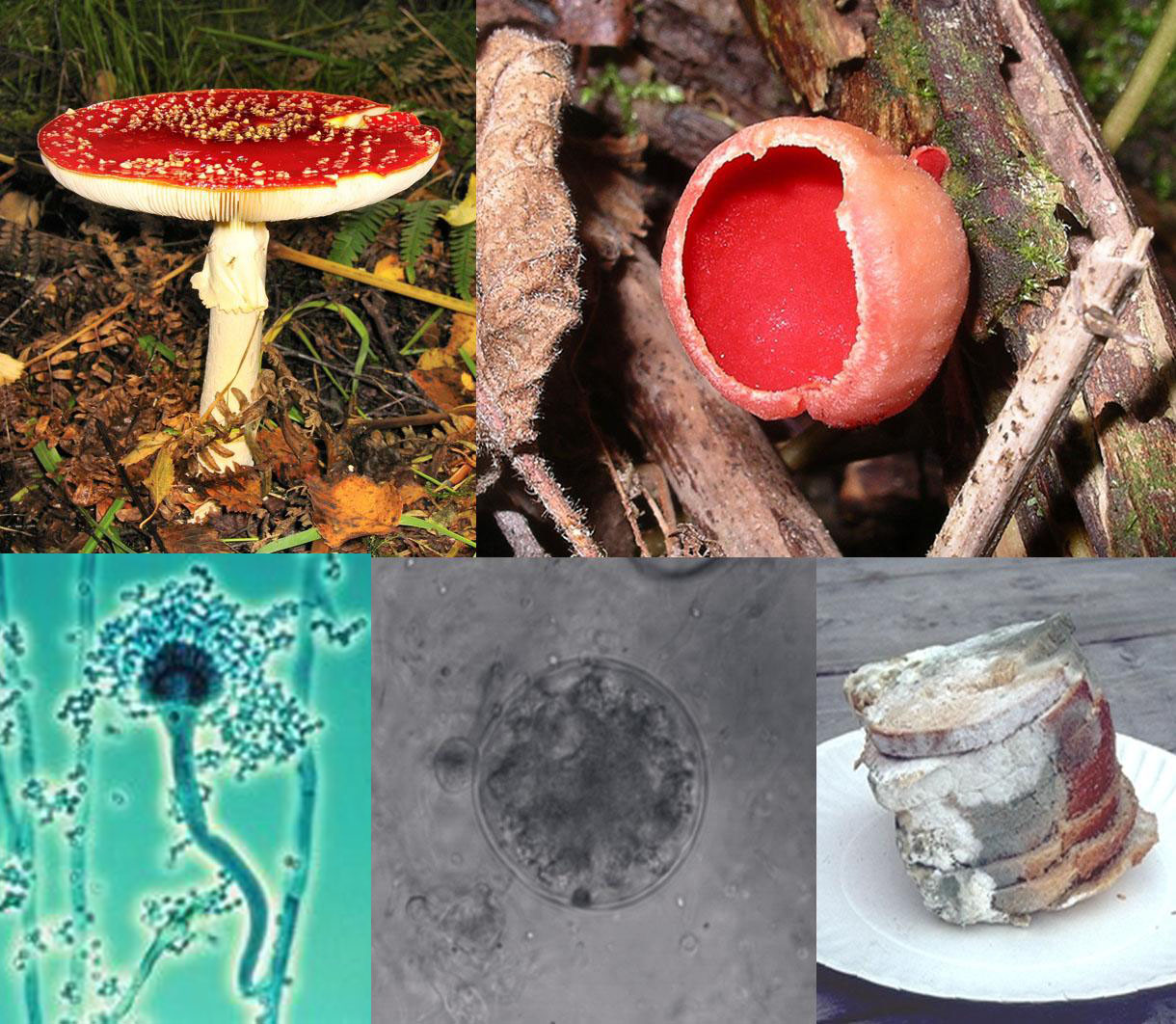

- Made of clusters of cells
- Fungi are sometimes too small to see, but once the group of cells gets too large it becomes visible to the naked eye
- Get their food by absorbing dissolved organic molecules
Function of Fungi
- Fungi exist in ecosystems to break down dead organic matter into small molecules that are able to be be used by other living things
- This is so that energy and nutrients can be reused!
Structure of Fungi
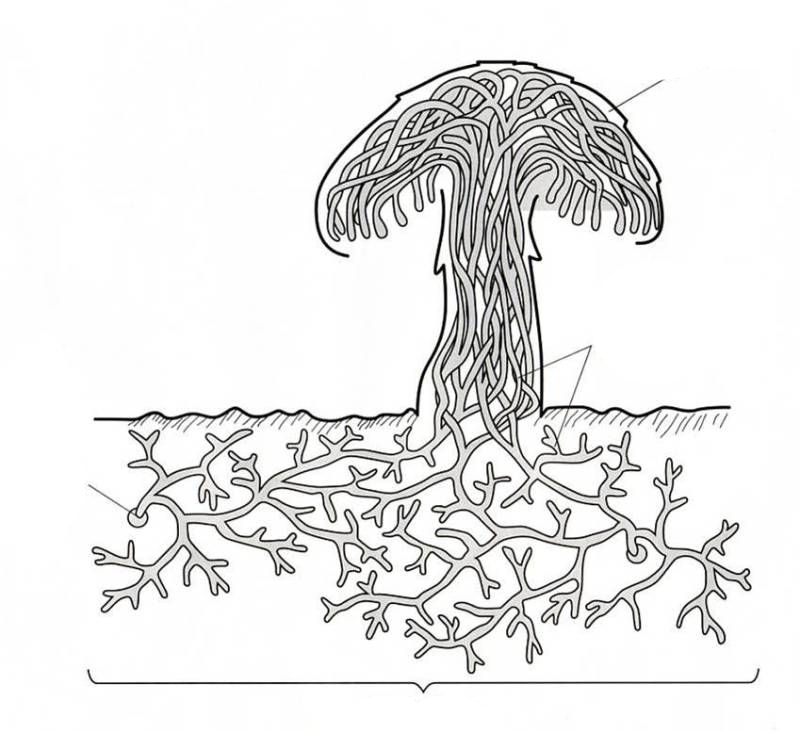
- Mycelium
- Spore
- Reproductive Structure
- Hyphae
Tūhura: Fungi
- In desk pairs, collect a bag, slice of bread and permanent marker
- Write your names on the bag
- Write the date (12/02/2021)
- Choose a place/thing to wipe the bread on - put
this label on your bread
- Everyone should do somewhere different
- Expose the bread to your surface, seal the bag and pin it to the board!

Tākaro/Game
Open https://joinmyquiz.com and get ready to play!
Akoranga 8 Mahi Tuatahi
- Collect a whiteboard from the front of the room
- In pairs, try your best to draw and label a diagram of a fungi from memory
- Extra: Explain the function/role of fungi in ecosystems
Ngā Whāinga Ako
- Describe how fungi feed by extra-cellular digestion
- Describe the role and importance of decomposers in an ecosystem
Write the date and ngā whāinga ako in your book
Why are Decomposers Important?
They allow energy and nutrients to be recycled through an ecosystem.

Extracellular Digestion

- Cell membrane: a semi-permeable membrane
- What does semi-permeable mean?
- Only some things (semi) can go through it (permeable)!
- Extra (outside), cellular (cell), digestion (break down)
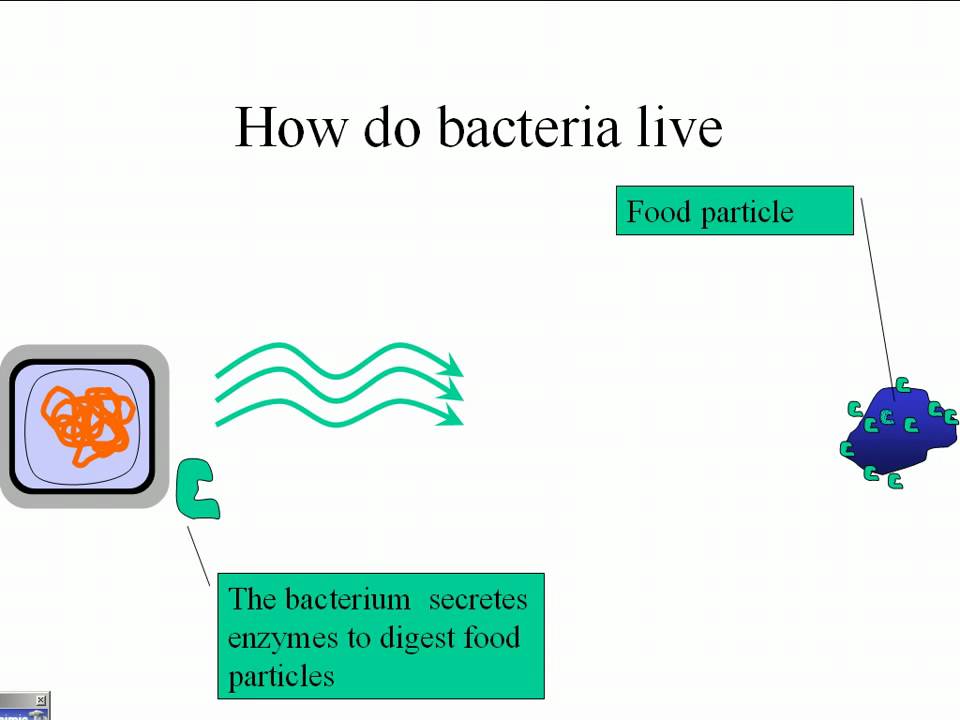
- Most food is made of large carbohydrate molecules
- It is hard to absorb such large molecules through the membrane, so extracellular digestion is needed to break the carbohydrates into smaller sugars
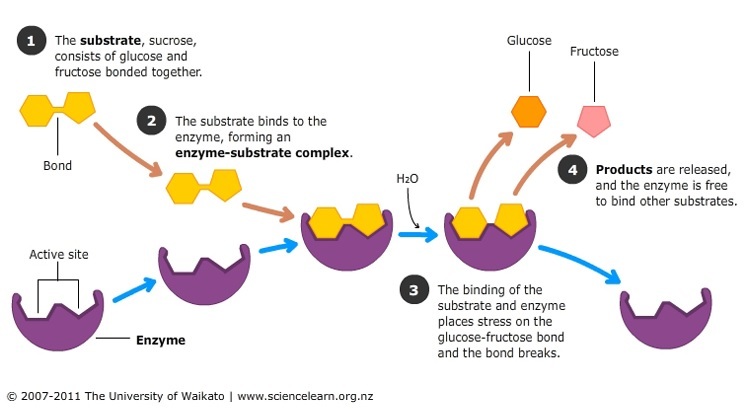
- Humans, bacteria, fungi and other organisms all use/creat enzymes to break down molecules in extracellular digestion.
- Enzymes are molecular machines that can perform specific functions in biology e.g break some molecules down (or join them together)!
Bread Tūhura/Investigation
- In humans we do extracellular digestion in our mouths, with the enzymes in our saliva!
- Take a piece of bread here, mush it up in your mouth but don’t swallow it! Over time your should notice the flavour start to change. What do you observe?
Ngohe/Activity
Open the TedED link on Google Classroom, watch the video and then answer the questions associated with it.