Electromagnetic Radiation
9SCIE - Radiation
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Mahi Tuatahi
- Collect your exercise books and a title
- Sit in your seating plan
- Glue in your title on a brand new page
- Colour in each letter a different colour
- Write down the date and today’s learning outcome:
- Today I will be able to name the main source of radiation and describe how it transfers energy.
Ngā Whāinga Ako
- I can name the main source of radiation and describe how it transfers energy
Electromagnetic (EM) Radiation?
- A type of radiant energy which can move through the vacuum of space
- Comes in many forms like visible light and heat energy
- Travels fast enough to go around Earth 8 times a second (300,000km per hour)
- The main source is the Sun!

- Cut out the sheet you have been handed.
- Use this image to help your organise the types of radiation!
Gamma Radiation
- Highest energy
- Come from stars in space
- Can be dangerous, but can be used to kill cancer

X-Rays
- Can be used to image bones
- Also produced by stars in space
- Dangerous in high amounts

Ultra-violet Radiation
- Can cause skinburn and cancer
- Our ozone layer protects us from it

Visible Light
- The part that we see with our eyes!

Infrared Radiaton
- Feels like heat!
- Your remote uses it to communicate with the TV

Microwaves
- Used to heat food
- Also used by satellites

Radio Waves
- Used for long range communication like radios

Light and Surfaces
Make four columns in your book with room for a title and diagram in teach!
Reflection
When light bounces off a surface. You see objects by seeing their reflected light.

Refraction
When light goes from one material to another e.g. from air to water, it can bend and change direction.

Transmission
Light can pass through some transparent materials like glass.

Absorption
E.g. an apple absorbs all colours of light except red, which is reflected into your eyes!

Whakamātau: Magnifying Glasses
- Collect your face mask from the front
- Cut out the face and spend 5-10 minutes decorating it
- Open the whakamātau document on Google Classroom and read through the background and method

Akoranga 2 Mahi Tuatahi
- Draw below, a diagram of what your magnifying glass looked like while you were trying to ignite your piece of paper. Indicate areas of relative brightness/darkness.
- Try and explain what is happening to the light to cause your diagram above.
- Why does the paper catch fire?
- Do any particular colours catch fire better than others?
Akoranga 2 Ngā Whāinga Ako
- I can recall the order and use of each type of electromagnetic radiation/hihi autōhiko
- I can name the seven colours of the visible spectrum and describe how to produce a spectrum by dispersion
Electromagnetic (EM) Radiation / Hihi Autōhiko
- A type of radiant energy which can move through a vacuum (korekore).
- Comes in many forms like visible light and heat energy
- Is a big spectrum (tūāwhiorangi)!

Task
Write down the order of the different electromagnetic waves (ngaru autōhiko) (least energy to most energy). Hint: ROYGBIV!

Visible Light / Aho Kitea
- Visible light is only a very small part of the spectrum
- Is between \(380\) to \(700 nanometers\)
- Purple/violet has the most energy (shortest wavelength)
- Red has the least energy (longest wavelength)

Task: Write the order of the visible spectrum colours

What is Wavelength / Roa o te Ngaru?
- The distance between consecutive peaks or troughs on a wave!
- Red light has a wavelength of \(700nm\) which is \(0.0000007m\)!
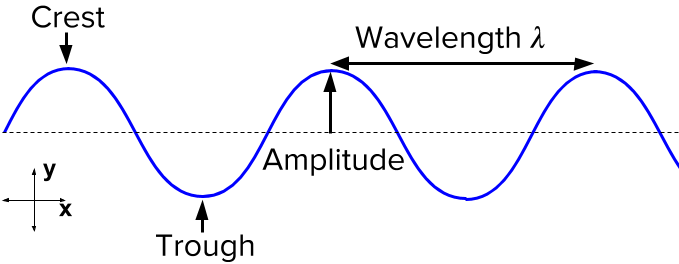
- Radio waves can have a wavelength of up to \(10,000km\)!
- Gamma waves can have a wavelength of \(0.00000000001m\)!

Task
Revise the flashcards on the electromagnetic spectrum (tūāwhiorangi autōhiko) on Quizlet!
https://quizlet.com/nz/526266053/electromagnetic-spectrum-flash-cards/