Nutrients in Food
9SCIE - Energy for Life
Finn Le Sueur
2024
Ngā Whāinga Ako
- Be able to list the major nutrients found in food
- Be able to say what each nutrient is used for
Food is a daily necessity.
Without food organisms will eventually die!
The process of acquiring, digesting and using food is called nutrition
Nutrients
There are four main nurtients the body needs:
- Carbohydrates,
- proteins,
- lipids,
- vitamins & minerals
Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates are sugars and starches which are mostly found in plant tissues
- They provide an immediate source of energy.
- Sugars are small molecules found in fruits
- Starches are long molecules found in cereals, potatoes and rice
- Starches are long repeating chains of sugars
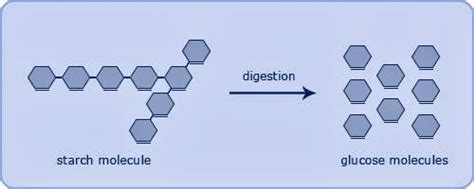
- The long chains of carbohydrates are broken down into the smaller sugar mocules by the body
- The small (sugar) molecules from carbohydrates are used by the body to release energy and make the body work
Proteins
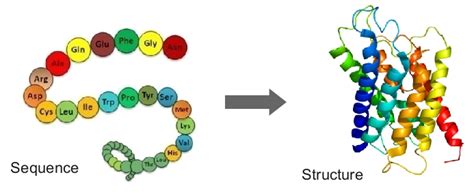
- Proteins are long chain molecules made of amino acid units
- Proteins are used in the construction of new cells for growth and repair
- They also control reactions in our body (enzymes)
Lipids
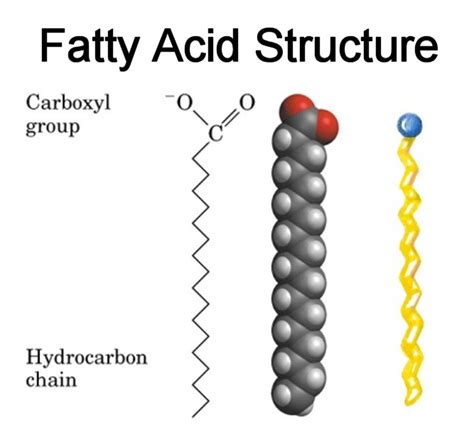
- Lipids include fats and oils and are made of fatty acids
- Our bodies store energy as lipids
- Lipids help keep the body warm and are used in making cell membranes
Which foods are rich in each nutrient?

Vitamins
- Vitamins are substances that your body needs to grow and develop normally
- Some vitamins can be made in our body (vitamin D and K) but most are acquired through our diet

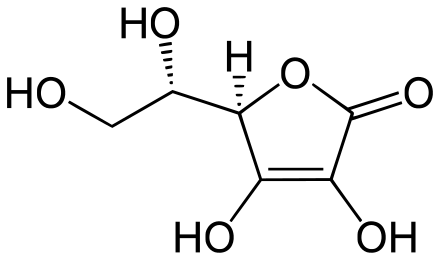
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
- Found in citrus fruits, green peppers, strawberries, tomatoes, broccoli, sweet and white potatoes
- Promotes a healthy immune system, helps wounds heal, maintains connective tissue and aids in the absorption of iron
Vitamin B12
- Found in eggs, milk, cheese, shellfish, meat and poultry
- It is important for metabolism, the formation of red blood cells and the maintenance of the central nervous system which includes brain and spinal cord

Vitamin E
- Found in corn, nuts, olives, green leafy vegetables, vegetable oils and wheat germ
- Protects cell membranes and tissues from damage, aids in the formation of red blood cells

Vitamin A
- Found in animal sources such as eggs, meat and diary products
- Beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A comes from green leafy vegetables and intensely colored fruits and vegetables
- Use in maintenance of tissue in the eyes, growth and healthy of skin and mucous membranes, development of teeth and skeletal tissue

Vitamin K
- Found in cabbage, cauliflower spinach and other green leafy vegetables as well as cereals
- Helps blood clotting
Vitamin D
- The body makes vitamin D when exposed to the sun
- Found in cheese, butter, margarine, fortified milk, fish and fortified cereals
- Promotes absorption of calcium, essential to development of healthy bones and teeth

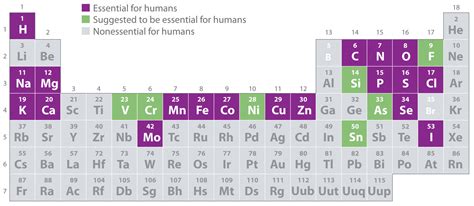
Minerals
Dietary minerals are the chemical elements required by living organisms other than C, H, O and N.
Fibre
- Fibre refers to the indigestible portion of plant foods.
- Pushes food through the digestive system, absorbs water and eases defecation.
Task: Match these up!
| Nutrient | Use |
|---|---|
| Minerals | Small amounts for cells to work properly |
| Proteins | Energy and to make cell membranes |
| Carbohydrates | In small amounts to make chemicals |
| Water | Energy |
| Vitamins | Growth and repair |
| Fibre | Chemical reactions and for transport |
| Fats | To keep the bowels working properly |
Task: Who has the most nutritious snack?
Find a wrapped snack in your bag with a food label - have a look at the ingredients, move around the classroom and try find the person with the most nutritious snack!